
دنیای مهندسی سازه های دریایی
Offshore Structures
دنیای مهندسی سازه های دریایی
Offshore Structureswind turbines part one/ توربین های بادی قسمت اول
انواع بادها
نیروهای صفرتا ۲ : سرعت باد تا ۱۱ کیلومتر (صفر تا ۷ مایل ) در ساعت ؛ هوا آرام یا دارای حرکت آهسته بوده و همراه با غبار و حرکت آهسته برگها می باشد.
نیروهای ۳ تا ۴ : سرعت باد از ۱۲ کیلومتر ۸ مایل) در ساعت تا ۲۹ کیلومتر ۱۸ مایل) در ساعت می باشد. نسیم یا باد متوسط وجود دارد که پرچم ها را به هم می زند، کاغذها را به هوا بلند می کند و به اطراف می برد و برگها و شاخه های کوچک درختان را حرکت می دهد. همانطور که می دانید در تهران پروژه پرچم انجام شد ولی متاسفانه مطالعه صورت نگرفته بیشتر ماه پرچم بدون حرکت می باشد ای کاش حداقل مکان های را انتخاب می کردن بیشتر بازده ای داشت.
در دنیا 5 کشور پروژه پرچم دارند 1. ایالات متحده آمریکا 2.تاجیکستان 3. آذربایجان 4. سوریه 5. ایران در زمان اجراء پروژه پرچم هزینه بالغ بر100 ملیون تومان برای هر پرچم هزنیه شد. وزن پرچم با توجه به جنس آن باید 2 کیلو باشد ولی وزن پرچم در ایران 20 کیلو است و همین باعث می شود پرچم ها زود فرسایش پیدا کند.
نیروهای ۵ تا ۶ : سرعت باد از ۳۰ کیلومتر ( ۱۹ مایل ) در ساعت تا ۵۰ کیلومتر ( ۳۱ مایل) در ساعت است. باد نیمه قوی یا قوی وجود دارد و درختان کوچک و شاخه های بزرگ به حرکت در می آیند و اشیاء سبک در سطح زمین به اطراف پرتاب می شوند.
نیروهای ۷ تا ۹: سرعت باد از ۵۱ کیلومتر ( ۳۹ مایل) تا ۸۷ کیلومتر ( ۵۴ مایل) در ساعت است. تند باد یا طوفان شدید وجود دارد. تمام درختان تکان می خورند، شاخه ها می شکنند و دودکشها و سقفهای خانه ها از جا کنده می شوند.
نیروهای ۱۰ تا ۱۲ : سرعت باد از ۸۸ کیلومتر ( ۵۵ مایل) در ساعت تا بیش از ۱۱۸ کیلومتر ( ۷۴ مایل) در ساعت می باشد. طوفان یا طوفان شدید وجود دارد. درختها از ریشه کنده می شوند و خرابیهای گسترده ایجاد می شود.
طراحی و ساخت توربین های بادی
برای تعیین ارتفاع بهینهٴ برج، سیستم کنترلی، تعداد و شکل پره ها از شبیه سازی های آیرودینامیکی استفاده می شود.
توربین های با محور افقی متداول، به سه بخش اصلی تقسیم می شوند:
بخش روتور، که تقریبًا ۲۰ ٪ قیمت توربین باد را به خود اختصاص داده و شامل پره های تبدیل کنندهٴ انرژی باد به انرژی جنبشی دورانی با سرعت کم می شود.
بخش ژنراتور که حدودا ۳۴ ٪ هزینهٴ توربین باد بوده و شامل مولد الکتریکی، تجهیزات کنترلی و جعبه دنده برای افزایش سرعت دورانی محور توربین می شود.
بخش تکیه گاهی که در بر گیرندهٴ ۱۵ ٪ قیمت توربین بوده و شامل برج و مکانیزم جهت دهی روتور نسبت به جهت وزش باد می شود.
بطور کلی یک توربین بادی خشکی محور افق از پنج قسمت اصلی تشکیل شده
است .
برج / دکل tower)
پره
ها Blades)
ماشین خانه (Nacelle)
فونداسیون
ترانسفورماتور (Transformer)
اجزاء تشکیل دهنده توربین های بادی محور افقی
با توجه به 62 مدل توربین بادی اجزاء اصلی آنها با هم یکی می باشد.


- پره ها ( Blades) : یکی از مهمترین بخشهای توربین بادی بوده و وظیفه آن تولید نیروی لازم برای چرخاندن شفت اصلی توربین باد است. پره به گونه ای ساخته می شود که استحکام و استقامت بسیار بالا در برابر نیروهای دینامیکی و آیرودینامیکی داشته باشد.
- روتور (Rotor ) : روتور توربین باد شامل پره، هاب (توپی پره)، دماغه و یاتاقانهای پره می باشد. به طور خلاصه بال ها و هاب به روتور متصل هستند.
- باد سنج (Anemometer) : این وسیله سرعت باد را اندازه گرفته و اطلاعات حاصل از آنرا به کنترل کنندها انتقال می دهد.
- ترمز (Brake ) : در توربین های بادی با ظرفیت بسیار پایین ( 1 الی 5 کیلووات) معمولا از سیستم های ترمز کفشکی استفاده می شود، زیرا جهت متوقف نمودن پره ها، نیروی زیادی مورد نیاز نیست. در توربین های بادی با ظرفیت بالا، از ترمزهای دیسکی استفاده می شود. عمل کردن می توان به صورت مکانیکی، الکتریکی یا هیدرولیکی انجام گیرد. به زودی برای درک عملکرد ترمزها در توربین های بادی فیلم از توربین های بادی اجراء شده در ایران به زبان فارسی در وبلاگ سازه های دریایی ارایه می شود .
- برج ( Tower) : برج ها از سازه های فولادی که به شکل لوله در آمده اند ساخته می شوند. توربین هایی که بر روی برج هایی با ارتفاع بیشتر نصب شده اند انرژی بیشتری دریافت می کند. ارتفاع برج معمولا بین یک تا یک ونیم برابر قطر روتور در نظر گرفته می شود. انتخاب نوع برج وابستگی به شرایط سایت دارد. همچنین سفتی برج فاکتور مهمی در دینامیک سازه توربین باد محسوب می گردد چرا که احتمال کوپل شدن ارتعاشات بین برج و روتور که منجر به خطر رزونانس می گردد وجود دارد.
- کنترولر (Controller): کنترولرها وقتی که سرعت باد به ۸ تا ۱۶ mph می رسد ما شین را، راه اندازی می کنند و وقتی سرعت از ۶۵ mph بیشتر می شود دستور خاموش شدن ماشین را می دهند. این عمل از آن جهت صورت می گیرد که توربین ها قادر نیستند زمانی که سرعت باد به 65 mph می رسد حرکت کنند زیرا ژنراتور به سرعت به حرارت بسیار بالایی خواهد رسید.
- گیربکس (جعبه دنده) ( Gear box) :از آنجائی که محور توربین دارای دور کم و گشتاور بالا و بر عکس آن محور ژنراتور دارای دور بالا و گشتاور کم است، سیستم انتقال قدرت باید به نحوی این دو محور را به یکدیگر متصل نماید. افزایش سرعت چرخش از ۳۰ تا ۶۰ rpm به سرعتی حدود ۱۲۰۰ تا ۱۵۰۰ rpm را ایجاد می کنند. و این افزایش سرعت برای تولید برق توسط ژنراتور الزامیست. هزینه ساخت گیربکس ها بالاست در ضمن گیربکس ها بسیار سنگین هستند مهندسان در حال تحقیقات گسترده ای هستند ژانراتورها نیازی به گیربکس نداشته باشند.
- ژنراتور Generator): پره های توربین بادی انرژی جنبشی باد را به انرژی دورانی درسیستم انتقال تبدیل می کنند وظیفه آن تولید برق متناوب می باشد و بیشتر از نوع ژنراتورهای القایی می باشد. بطور معمول از سه نوع ژنراتور در توربینهای بادی استفاده می شود. - ژنراتور جریان مستقیم - آلترناتور یا ژنراتور سنکرون - ژنراتور القایی یا آسنکرون
- ماشین خانه ( Nacelle): شامل پوشش خارجی مجموعه توربین، شاسی و سیستم دوران حول محور برج می باشد که روتور به آن متصل است. ماشین خانه در بالای برج قرار دارد.بعضی از ماشین ها آنقدر بزرگند که تکنسین ها می توانند داخل آن باستند.
- محور اصلی (Main Shaft): روتور به یک دیستک بسیار قوی بر روی شفت اصلی توربین بادی پیچ شده است.
- شفت با سرعت بالا (High-Speed Shaft) : که وظیفه آن به حرکت در آوردن ژنراتور می باشد.
- شفت با سرعت پایین (Low-Speed shaft): رتور حول این محور چرخیده و سرعت چرخش آن 30 تا 60 دور در دقیقه می باشد.
- جهت باد ( wind direction) : توربین هایی که از این فناوری استفاده می کند در خلاف جهت باد نیز کار می کنند در حالی توربین های معمولی فقط جهت وزش باد به پره های آن باید از روبرو باشد.
- بادنما ( wind vane) : وسیله ای است که جهت وزش باد را اندازه گیری می کند و کمک می کند تا جهت توربین نسبت به باد در وضعیت مناسبی قرار داشته باشد.
- موتور انحراف (yaw motor ): برای به حرکت در آوردن درایو انحراف مورد استفاده قرار می گیرد.
- درایو انحراف (yaw drive): وسیله ایست که وضعیت توربین را هنگامی که باد در خلاف جهت می وزد کنترول می کند و زمانی استفاده می شود که قرار است روتور در مقابل وزش باد از روبرو قرار گیرد اما زمانی که باد در جهت توربین می وزد نیازی به استفاده از این وسیله نمی باشد.

- سیستم انتقال قدرت: سیستم انتقال قدرت شامل اجزاء گردنده توربین باد است. این اجزاء عمدتاً شامل محور کم سرعت (سمت روتور)، گیربکس و محور سرعت بالا ( در سمت ژنراتور) می باشد. سایر اجزاء این سیستم شامل یاتاقانها، یک یا چند کوپلینگ، ترمز مکانیکی و اجزاء دوار ژنراتور می باشد. در این مجموعه وظیفه گیربکس افزایش سرعت نامی روتور از یک مقدار کم (در حد چند ده دور در دقیقه) به یک مقدار بالا (در حد چند صد یا چند هزار دور در دقیقه) که مناسب برای تحریک یک ژنراتور استاندارد است، میباشد. عمدتاً دو نوع گیربکس در توربینهای بادی مورد استفاده قرارمیگیرد: گیربکسهای با شفتهای موازی و گیربکسهای سیارهای. برای توربینهای سایز متوسط به بالا بزرگتر از KW 500 مزیت وزن و سایز در گیربکسهای سیارهای نسبت به نوع دیگر یعنی گیربکسهای با شفت موازی کاملاً بارزتراست. بعضی از توربینهای باد از یک طرح خاص برای ژنراتور استفاده می کند (ژنراتور با تعداد قطب بالا ) که در آن نیازی به استفاده از گیربکس نمیباشد.
- سیستم کنترل: برای بدست آوردن حداکثر راندمان از یک توربین بادی، باید بتوان همواره صفحه دوران توربین را عمود بر جهت وزش باد قرار داد. برای این منظور از سیستم هایی برای تغیر جهت توربین بادی و قرار دادن سیستم در مسیر باد استفاده می شود. این سیستم (yaw system) یک سیستم ترکیبی الکتریکی- مکانیکی است که هدایت آن توسط واحد کنترل انجام میشود. در توربین های بادی سایز کوچک به جای چرخ انحراف (yaw system) از بالچه استفاده می کنند. همچنین سیستم هایی جهت کنترل و تنظیم سرعت دورانی در توربین بادی مورد استفاده قرار می گیرند. چنین سیستمهایی علاوه بر کنترل دور روتور، مقدار قدرت تولیدی و نیروهای وارده بر روتور در بادهای شدید را نیز محدود می کنند.
- سیستم هیدرولیک: سیستم های هیدرولیک به مجموعه جک و یونیت هیدرولیکی و اتصالات جانبی آنها اطلاق می شود. جک هیدرولیکی از یک سیلندر و پیستون دو طرفه تشکیل شده است و با انتقال سیال به هر ناحیه از آن، جک به سمت مخالف حرکت می کند. یونیت هیدرولیکی از الکتروموتور، پمپ، مخزن تامین فشار اولیه، شیرهای هیدرولیکی، شیلنگهای انتقال سیال به دو ناحیه داخل سیلندر جک، مخزن روغن، روغن مخصوص و تجهیزات جنبی تشکیل شده است. پس از دریافت فرمان، پمپ مقداری روغن را از داخل مخزن به محفظه جلو یا عقب سیلندر جک پمپ می کند تا جک بتواند به مقدار مورد نیاز محور تراورس را در جهت مورد نیاز حرکت دهد. محور تراورس محوری است که از سوراخ داخل شفت اصلی عبور می کند و یک سمت آن با جک هیدرولیکی و طرف دیگر آن با مکانیزم مثلثی واقع درون هاب مرتبط است. وظیفه این محور انتقال حرکت جک هیدرولیکی و در واقع فرمان کنترلر به مکانیزم مثلثی است که باعث چرخش پره ها می گردد. مکانیزم مثلثی درون هاب باعث تبدیل حرکت انتقالی محور تراورس به حرکت چرخشی و نتیجتا چرخش پره ها به دور محورشان می گردد.

Wind turbine
A wind turbine is the popular name for a device that converts kinetic energy from the wind into electrical power. Technically there is no turbine used in the design but the term appears to have migrated from parallel hydroelectric technology. The correct description for this type of machine would be aero foil powered generator.
The result of over a millennium of windmill development and modern engineering, today's wind turbines are manufactured in a wide range of vertical and horizontal axis types
Make a wind sock
You can use a wind sock to find out where the wind comes from

Tower
Made from tubular steel concrete, or steel lattice. Supports the structure of the turbine. Because wind speed increases with height, taller towers enable turbines to capture more energy and generate more electricity
Nacelle
Sits atop the tower and contains the gear box, low-speed and high-seep shafts, generator, controller, and brake. Some nacelles are large enough for a helicopter to land on
Gear box
There is a gearbox inside the nacelle. Connects the low-speed shaft to the high-speed and increases the rotational speeds from about 30-60 rotations per minute (rpm),to about 1000-1800 rpm; This is the rotational speed required by most generators to produce electricity
Rotor
Blades and hub together form the rotor low-speed shaft turns the low-speed shaft at about 30-60 rpm. The length of the blades varies a lot with each wind turbine. On a wind turbine like this one a blade is 25-27 meters long
Blades
Lifts and rotates when wind is blown over them, causing the rotor to spin. Most turbines either two or three blades
Brake
Stops the rotor mechanically, electrically, or hydraulically, in emergencies
Pitch
Tums (or pitches) blades out of the wind to control the rotor speed and to keep the rotor from turning in winds that are too high or too low to produce electricity
Main Shaft
The rotor is bolted to a very strong disc on the main shaft of the wind
turbine
Wind Vane
A wind vane always positions itself according to the wind direction. A measure
wind direction and communicates with the yaw drive to orient the turbine
properly with respect to the wind
Controller
The wind turbine is controlled by several computers that keep an eye on many
different things
Together these computers are called the wind turbine control system. The main
computer is called the controller. Starts
up the machine at wind speeds of about 8 to 16 miles per hour (mph) and shuts
off the machine at about 55 mph. Turbines do not operate at wind speeds above
about 55 mph because they may be damaged by the high winds
Generator
A generator makes electricity. There are some magnets and a lot of copper wire
inside the generator. Produces 60-cycle AC electricity; it is usually an
off-the-shelf induction generator
High-speed shaft
Drives the generator
Low-seed shaft
Turns the low-speed shaft at about 30-60 rpm
Wind Direction
Determines the design of the turbine: upwind turbines-like the one shown here-face into the wind while downwind turbine face away
Yaw Motor
Powers
the yaw drive
yaw Drive
Orients upwind turbines to keep them facing the wind when the direction changes. Downwind turbines don´t require a yaw drive because the wind manually blows the rotor away from it
Small Shaft
The small shaft connects the generator to the gearbox
This shaft does not have to transfer as much turning force as the main shaft does
Anemometer
The anemometer measures the wind speed and notifies the wind turbine controller
when it is so windy that it would be profitable to use power to make wind
turbine turn (yaw) into the wind and start running. It is important to know how
much wind there is. If the wind is too strong the wind turbine can break
Cooling
System (Radiator
When the generator is running it gets hot. If it gets too hot it can break
down
Therefore it is necessary to cool down the generator before it becomes so hot
that it stops working. The generator can be cooled in two ways – either by air
or water
Mechanical
Brake
A wind turbine has two different types of brakes. One is the blade tip brake
The other is a mechanical brake. The mechanical brake is placed on the small
fast shaft between the gearbox and the generator
Yaw
Bearing
The yaw motor has a small wheel that engages a huge wheel. The large wheel is
called the yaw bearing

آخرین مدل از خانواده توربین های بادی بنام مولد انرژی بدون پره گردابه /vortex Bladeless می باشد نمی توانیم به این سیستم انرژی تجدیدپذیر توربین گفت. یادم زمانی که دانشجو بودم مهندس پویا فلاح که درباره گرداب ها مطالعه می کرد با یکی از استادان موضوع ارتباط انرژی تجدیدپذیر با گرداب را و طرح کرد اون استاد و هم ما خندیدم اینجا جا دارد از ایشان از طرف هم معذرت می خوام
مقالات 2015/Articles in 2015 years
مجموعه ای از مقالات 2015 سازه های دریایی
Offshore series of articles in 2015
This file is password
Password: CE-MS MS.c Bijan Mohammadi


عنوان های مقالات / Articles Title
1Three Legged Articulated Support for 5 MW Offshore Wind Turbine, 2015
2Engineering critical assessment for offshore pipelines with 3-D elliptical embedded cracks, 2015
3A method to correct the flow distortion of offshore wind data using CFD simulation and experimental wind tunnel tests, 2015
4The platform pitching motion of floating offshore wind turbine: A preliminary unsteady aerodynamic analysis, 2015
5Evidence for the biotic origin of seabed pockmarks on the Australian continental shelf, 2015
6Levels of Cd, Cu, Pb and V in marine sediments in the vicinity of the Single Buoy Moorings (SBM3) at Mina Al Fahal in the Sultanate of Oman, 2014
7Assessing shelf aggregate environmental compatibility and suitability for beach nourishment: A case study for Tuscany (Italy), 2015
8Dynamic response of offshore jacket platform including foundation degradation under cyclic loadings, 2015
9Dynamic response analysis of a floating offshore structure subjected to the hydrodynamic pressures induced from seaquakes, 2015
10Reliability analysis of offshore wind turbine support structures under extreme ocean environmental loads, 2014
11Wind farm power optimization including flow variability, 2015
12Offshore wind power potential of the Gulf of Thailand, 2015
13Focus on the development of offshore wind power in China: Has the golden period come? , 2015
14V-shaped semisubmersible offshore wind turbine: An alternative concept for offshore wind technology, 2015
15Dark green electricity comes from the sea: Capitalizing on ecological merits of offshore wind power? , 2015
16Evaluating capital and operating cost efficiency of offshore wind farms: A DEA approach, 2015
17The aspects of employing of offshore companies in industrial corporations, 2014
18The large penumbra: Long-distance effects of artificial beach nourishment on Posidonia oceanica meadows, 2014
19Structural model updating of an offshore platform using the cross model cross mode method: An experimental study, 2015
20Numerical simulation of hydrodynamic wave loading by a compressible two-phase flow method, 2015
21Hybrid damping systems in offshore jacket platforms with float-over deck, 2014 (Iranian
22Temporal variation in environmental conditions and the structure of fish assemblages around an offshore oil platform in the North Sea, 2015
23Experimental research on fatigue property of steel rubber vibration isolator for offshore jacket platform in cold environment, 2009
24Study on the structural monitoring and early warning conditions of aging jacket platforms, 2015
25Feasibility study of offshore wind turbine substructures for southwest offshore wind farm project in Korea, 2015

Non-compliance with the installation on jack-up design/ عدم رعایت طراحی در نصب جک آپ
این انیمیشن درباره عدم رعایت طراحی در نصب جک آپ می باشد.The animation on non-compliance with the installation on Jack-up design
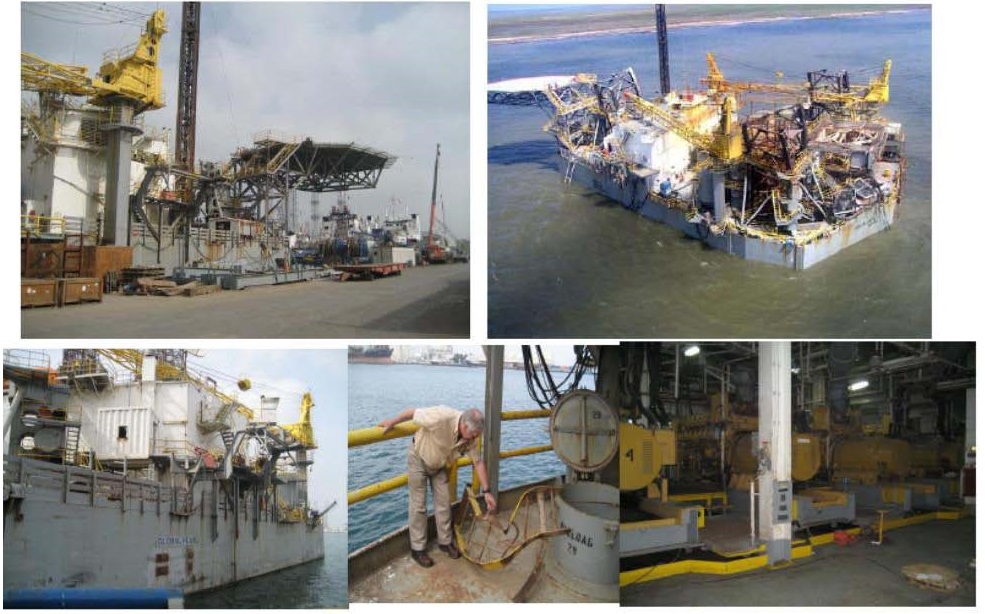
همانطور که در این انیمیشن ملاحظه می کنید عدم رعایت طراحی در نصب سکو بالا برو باعث خسارت سنگینی می شود .
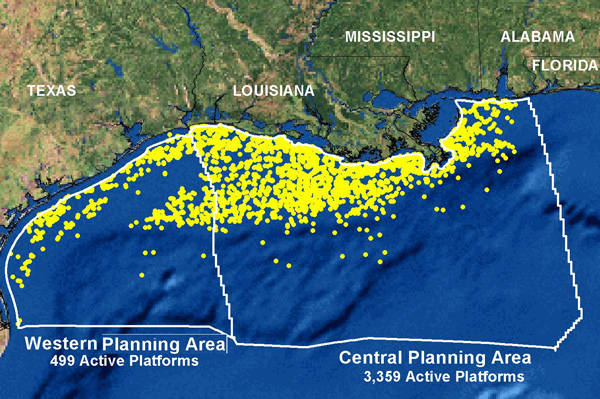
این سکو در سواحل لوئیزیانا واقع در خلیج مکزیک بوده ، لوئیزیانا یکی از شهر های ایالات متحده آمریکا می باشد و این شهر در کرانه رود میسی سیپی واقع شده و عقب نشینی این رودخانه باعث بوجود آمدن دلتا ها و مناطق با تلاقی زیادی شده است وبنادر مهم ایالات متحده آمریکا در آن واقع است

توفان کاترینا یکی از مرگبارترین حوادث طبیعی در تاریخ ایالات متحده آمریکا در سال 2005 اتفاق افتاد.
توفان گوستاو
جدید ترین توفان که گزارش شده توفان دریایی گوستاو است که یکی از بزرگترین توفان های دریای ثبت شده است.
زمانی که سکو در موقعیت خود قرار می گیرد، پایه ها آن توسط جک ها هیدرولیکی به پایین می رود. توضحات کامل قبلا نوشته شده است.
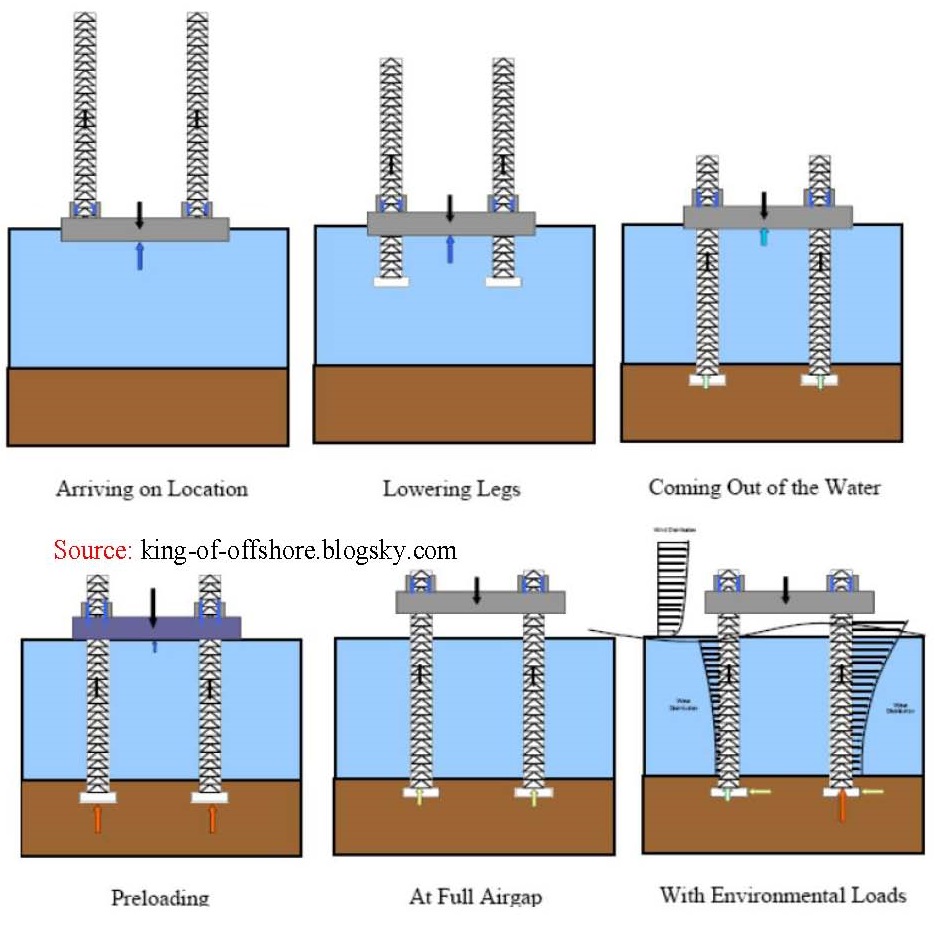
همانطور که در شکل ملاحظه می کنید بیشترین لنگر تکیه های در قسمت بالای پایه های سکو می باشد.
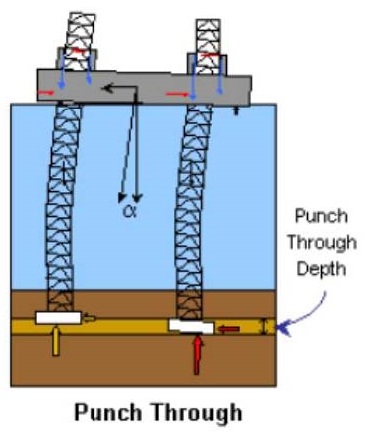
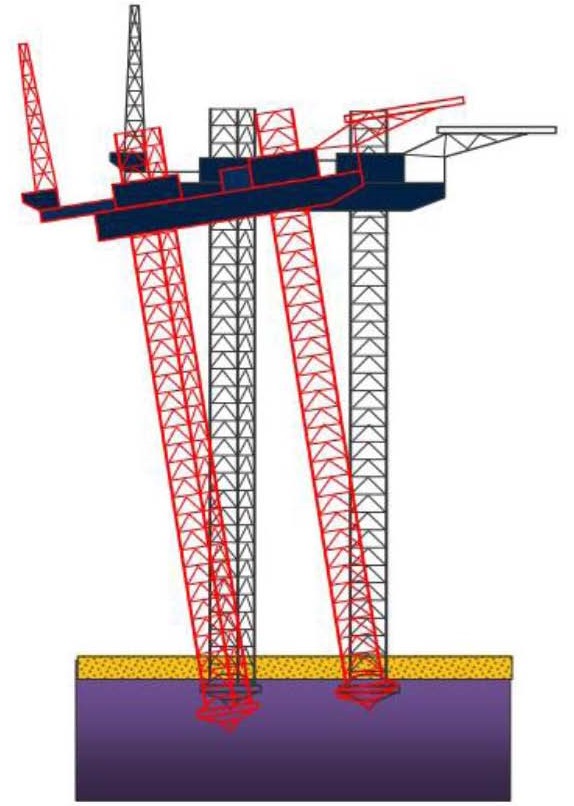
در هنگام نصب پایه ها باید پایه شاقول باشند. در آیند در همین وبلاگ دنیای سازه های دریایی طریق شاقول کردن سکو بارو را نشان می دهیم. قسمت های از رابطه حاکم در طراحی سکوی بالابرو برای نصب یک سکو بالارو نیاز به محاسبه می باشد
Jack up the parts that govern the design to install a platform lift is required to calculate

در این جا دارد از استاد آقا دکتر فخر یاسری و دکتر ماهانی به خاطر قبول شاگردی اینجانب برای یاد گیری بحث طراحی سکوها و طراحی تجهیزات زیر دریا و معماری آن تشکر کنم در هم ماه ، در عنوان دیگر به طور مفصل از آقای دکتر فخر یاسری یاد خواهد و از آقای وحید خوانسار رییس دانشکده عمران دانشگاه شریف قدرانمدی می نمایم جهت معرفی کردن اینجانب به دو بزرگواران
با توجه به اینکه بزرگتر آرشیو منبع سازه های دریایی را دارا بودم زمانی که دکتر فخر یاسری درباره عدم طراحی سکوها بالارو صحبت می کردند آمار این سکو در بین صحبت های مشخص شد الان یکی از همکاران دکتر ماهانی آن را خریداری نموده شده جهت تعمیر این سکو در حاضر در خلیج فارس در سواحل دبی می باشد.دکتر ماهانی یکی اساتید سابق دانشگاه شریف بوده در حاضر در شرکت Smart Petroleum در کشور انگلیس می باشند. www.smartpetroleum.com +4407710305656


Design of Coastal Structures and Sea Defenses (Series on Coastal and Ocean Engineering Practice)-vol 2
این کتاب بنام طراحی سازه های ساحلی و محافظت آنها از دریا ،ویرایش دوم
Design of Coastal Structures and Sea Defenses (Series on Coastal and Ocean Engineering Practice)-vol 2, Young C Kim, World Scientific Publishing Company, 2015
This file is password & You can not print
Password: CE-MS MS.c Bijan Mohammadi
All text and change the color to use to download it
Download / دانلود Password/ کلمه عبور

این کتاب دارای 287 صحفه می باشد. سازه های ساحلی یک جزء مهم در هر طراحی جهت حفاظت از ساحل و طراحی آنها به طور مستقیم در کنترل موج و طوفان تاثیر به سزای روی خط ساحلی دارند.

برای فراهم کردن ثبات در ساحل و حفاظت از آن این کتاب پیشرفت های فنی ترین در زمینه طراحی و ساخت سازه های ساحلی در محافظت آنها از دریا می باشد. این کتاب آخرین ویرایش در فن آوری مهندسی سواحل در برنامه ریزی، طراحی و ساخت ساز، روش موثر مهندسی، پروژه های منحصره به فرد و چالش ها و مشکلاتی که در زمینه طراحی و ساخت ساز است یاد آوری نموده است در بخش های ساحلی، اقیانوس ها، کارهای عمرانی آنها و مهندسی ژئوتکنیک دریایی مباحث مهمی دارد.

در مطالب کتاب در قسمت شبیه سازی به عنوان هیدرولیک امکانات تست در دایک و سایر سازه های ساحلی این قسمت توسط پروفسور ون در میر نوشته شده است . ایشان دارای بیشتر مقالات علمی در زمینه مهندسی ساحلی و مهندسی اقیانوس می باشند.
Coastal structures are an important component in any coastal protection scheme. They directly control wave and storm surge action or to stabilize a beach which provides protection to the coast
This book provides the most up-to-date technical advances on the design and construction of coastal structures and sea defenses. Written by renowned practicing coastal engineers, this edited volume focuses on the latest technology applied in planning, design and construction, effective engineering methodology, unique projects and problems, design and construction challenges, and other lesions learned. Many books have been written about the theoretical treatment of coastal and ocean structures. Much less has been written about the practical practice aspect of ocean structures and sea defenses. This comprehensive book fills the gap. It is an essential source of reference for professionals and researchers in the areas of coastal, ocean, civil, and geotechnical engineering

Contents
- Simulators as Hydraulic Test Facilities at Dikes and Other Coastal Structures (Jentsje W van der Meer
- Design, Construction and Performance of the Main Breakwater of the New Outer Port at Punto Langosteira, La Coruña, Spain (Hans F Burcharth, Enrique Maciñeira Alonso, and Fernando Noya Arquero
- Performance Design for Maritime Structures (Shigeo Takahashi, Ken-ichiro Shimosako, and Minoru Hanzawa
- An Empirical Approach to Beach Nourishment Formulation (Timothy W Kana, Haiqing Liu Kaczkowski, and Steven B Traynum)
- Tidal Power Exploitation in Korea (Byung Ho Choi, Kyeong Ok Kim and Jae Cheon Choi
- A Floating Mobile Quay for Super Container Ships in a Hub Port (Jang-Won Chae and Woo-Sun Park
- Surrogate Modeling for Hurricane Wave and Inundation Prediction (Jane McKee Smith, Alexandros A Taflanidis and Andrew B Kennedy
- Statistical Methods for Risk Assessment of Harbor and Coastal Structures (Sebastián Solari and Miguel A Losada

تاثیر پریود امواج بر روی اتصالات سازه های شناور به هم پیوسته
تاثیر پریود امواج بر روی اتصالات سازه های شناور به هم پیوسته
با تشکر از مهندس محمدعلی بهاری بابت فایل مقالات و چکیده مقاله ایشان در وبلاگ دنیای سازه های دریایی برای محققان که در این زمینه کار می کنند اگر سوال دارند می توانند با ایمیل ایشان در ارتباط داشته باشند ایمیل ایشان bahari902011@yahoo.com
Period waves impact on the floating structures interlocking connections
Thanks to Engineering Mohammad Ali Bahari file for articles and abstracts offshore His blog in this field of work if they are able to e-mail their questions linked their email bahari902011@yahoo.com

This file is password
Password: CE-MS MS.c Bijan Mohammadi
As the article posted by Mr. Mohammad Ali Bahari1Time domain finite volume method for three-dimensional structural–acoustic coupling analysis
2Dynamic solid mechanics using finite volume methods
3An unstructured finite volume time domain method for structural dynamics
4Coupled dynamic analysis for wave interaction with a truss spar and its mooring line/riser system in time domain
5Hybrid frequency–time domain models for dynamic response analysis of marine structures
6A hybrid approach for the time domain analysis of linear stochastic structures7An optimised FEM–BEM time-domain iterative coupling algorithm for dynamic analyses
Time-domain numerical and experimental analysis of hydro elastic response of a very large floating structure edged with a pair of submerged horizontal plates
9. Time-domain simulation of wave–structure interaction based on multi-transmitting formula coupled with damping zone method for radiation boundary condition
10Response analysis and optimum configuration of a modular floating structure with flexible connectors
11Substructural identification of jack-up platform in time and frequency domains
12A finite volume unstructured mesh approach to dynamic fluid–structure
interaction : an assessment of the challenge of predicting the onset of flutter
13A numerical study on environmental impact assessment of Mega-Float of Japan14ANALYTICAL MODELS OF FLOATING BRIDGES SUBJECTED BY MOVING LOADS FOR DIFFERENT WATER DEPTHS
15Approximate Methods for Dynamic Response of Multi-module Floating Structures
16Dynamic response and structural integrity of submerged floating tunnel due to hydrodynamic load and accidental load
17Effect of compression on wave diffraction by a floating elastic plate
18Efficient hydrodynamic analysis of very large floating structures
19Evaluation of bending moments and shear forces at unit connections of very large floating structures using hydro elastic and rigid body analyses
20Fully nonlinear simulation of wave interaction with fixed and floating flared structures
21Hydrodynamic analysis of multi-body floating piers under wave action
22Hydrodynamic Interaction Analyses of Very Large Floating Structures
23Hydro elastic analysis of flexible floating interconnected structures
24Hydro elastic responses and drift forces of a very-long floating structure equipped with a pin-connected oscillating-water-column breakwater system
25Integrated hydrodynamic–structural analysis of very large floating structures (VLFS
26Multi-module Floating Ocean Structures
27. Overview: Research on wave loading and responses of VLFS
28. Response analysis and optimum configuration of a modular floating structure with flexible connectors
29. Response due to moored multiple structure interaction
30Simulation of floating bodies with the lattice Boltzmann method
31Stiffness of mooring lines and performance of floating breakwater in three dimensions
32. Structural analysis for the design of VLFS
33. Structural modeling for global response analysis of VLFS
34. Transverse earthquake response and design analysis of submerged floating tunnels with various shore connections
35Wave effects on deformable bodies
تاثیر پریود امواج بر روی اتصالات سازه های شناور به هم پیوسته
چکید ه
در این مقاله اثر پریود موج در پین اتصالات اسکله های شناور مدولار بررسی شده است. اسکله به صورت سازه ای با بدنه های صلب و اتصالات مفصلی- صلب مدل گردیده است. سه پانتون با ابعاد 1.8*7*20 متر و عمق آب نیز با توجه به مشخصات کشتی طرح 7 مترو پریود موج غالب 5 ثانیه در نظر گرفته شده است. امواج بر خوردی در راستای طولی سازه شناور انجام شده است. معادلات امواج، استوکس مرتبه 5 لحاظ شده است. فرایند تحقیق با دو نرم افزار آباکوس و استارسی سی ام پلاس انجام شده است و با توجه به عملکرد نرم افزار از روش تحلیل دینامیکی کامل استفاده شده است. با کوپل این دو نرم افزار، تنش در پین اتصالات بدست آمده است. نتایج حاصل نشان می دهد که با افزایش دوره تناوبی به ثانیه، شدت تنش وارده به پین اتصال افزایش یافته است. این نتایج حاکی از آن است که طراحی هر سیستم سازه ای شناور نیازمند به انتخاب معیار و ملاک مناسب و منطقی است. بنابراین در مناطق با پریود موج بالاتر از پریود موج غالب، انتخاب چنین سازه ای به ندوت رخ می دهد.
Period waves impact on the floating structures interlocking connections
Abstract
In this paper the effect of modular floating dock connectors pin wave period studied. Handles for rigid body structure with a rigid model is Mfsly- connections. Tuesday Pantone size 1.8 * 7 * 20 m and depth profile with respect to ship the 7 subway dominant wave period of 5 seconds is considered. Eat in longitudinal direction of the waves on the floating structures. Wave equation, Stokes is in the order of 5. ABAQUS software with the research process and Astarsy thirtieth Plus has been done with regard to the application of the full dynamic analysis method is used. By coupling these two software, tension bolt connections have been obtained. The results show that by increasing the Period in seconds, greatly increased the stress to the pin connection. These results suggest that the design of any system of floating structures need to choose the appropriate and logical criteria. Therefore, in areas with a dominant wave period, wave period above, the choice of such a structure rarely occurs
