
دنیای مهندسی سازه های دریایی
Offshore Structures
دنیای مهندسی سازه های دریایی
Offshore StructuresThis film How to shipbuilding ocean going/فیلم چگونه ای ساخت کشتی کانتینربر اقیانوس پیما
این انیمیشن برای اول بار ارائه شده است خدا شکر می کنم به من فرصتی داده بعد از یک سال نیم وعده توانستم در این زمان آن را ارایه نمایم این انیمیشن نحوه ساخت کشتی کانتینربر اقیانوس پیما را نشان می دهد و همچنین معروفی قسمت های از کارگاه کشتی سازی راThis animation shows how to build a container ship on the ocean and the famous episode of the shipyard's

شناور کانتتینر بر اراک-PG101
این شناور اولین کشتی اقیانوس پیمای ساخت کشور است که علیرغم تحریم های صورت گرفته با کیفیت قابل رقابت با نمونه خارجی، تحویل داده شد و از تاریخ 10/03/1389 عملیاتی گردید.
همانطور که اشاره شد به خاطر تحریم ها این حرکت شد در دنیا اصولا کشتی سازی دست چند کشور است و بفیه کشورها از این کشوری کشتی سازی خرید می کنند چون مقرن به صرفه است به خاطر تکنولوژی روز این صنعت اگر این کشتی سازی نتواند سفاری داشته باشد وآن کیفیت از نظر استاندارد جهان را نداشته باشد این صنعت هم مانند بقیه صنایع ایران دچاره مشکلات مالی و تعدیل نیرو می گردد امیدوارم کشتی که در این صنایع ساخت می شود بتوان با کیفیت ها بالا خود بتوان ارز آوری داشته باشد.
یک کارگاه کشتی سازی از چند کارگاه دیگر تشگیل شده است.
کارگاه شات بلاست : شات بلاست و اعمال رنگ اولیه بر روی انواع ورق و لوله و پروفیل با عرض دهند ورودی 3100 mm
کارگاه برش: برش و لبه سازی انواع ورقهای و لوله ها با دستگاه های CNC (هوا گاز و پلاسما)
کارگاه فرم دهی: عملیات خمکاری و ورقها و لوله ها با دستگاه های رول 13 متری پرس 800 تن و دستگاه رول 3 محوره
کارگاه پانل سازی: دارای یک خط تولید نیمه اتوماتیک ساخت پانل های مسطح (TTS) می باشد که مجهز به دستگاه های مونتاژ و جوش پروفیل بر روی روق می باشد.
کارگاه ساخت سکش : این کارگاه مسقف با داشتن جرثقیل 80،100، 150 تنی به همراه فضای مناسب امکان ساخت سازه های حجیمی را تا ارتفاع 25 متر و با تناژ 400 تن فراهم می کند.
کارگاه رنگ زدایی و رنگ آمیزی
دارای سیستم هوای فشرده و کنترل دما و رطوبت
ماشین ها تراش
دستگاه برش ورق هیدرولیکی
پرس ورق هیدرولیکی
دستگاه لوله خم کن
دستگاه بوژی :
این دستگاه ها پیشرفته هستند و به صورت کنترل از راه هدایت می شوند،با قابلیت جابجایی احجام سنگین تا ظرفیت 520 تن از این دستگاه ها برای حمل و نقل فونداسیون توربین های بادی فراساحل کیسونی استفاده می شود
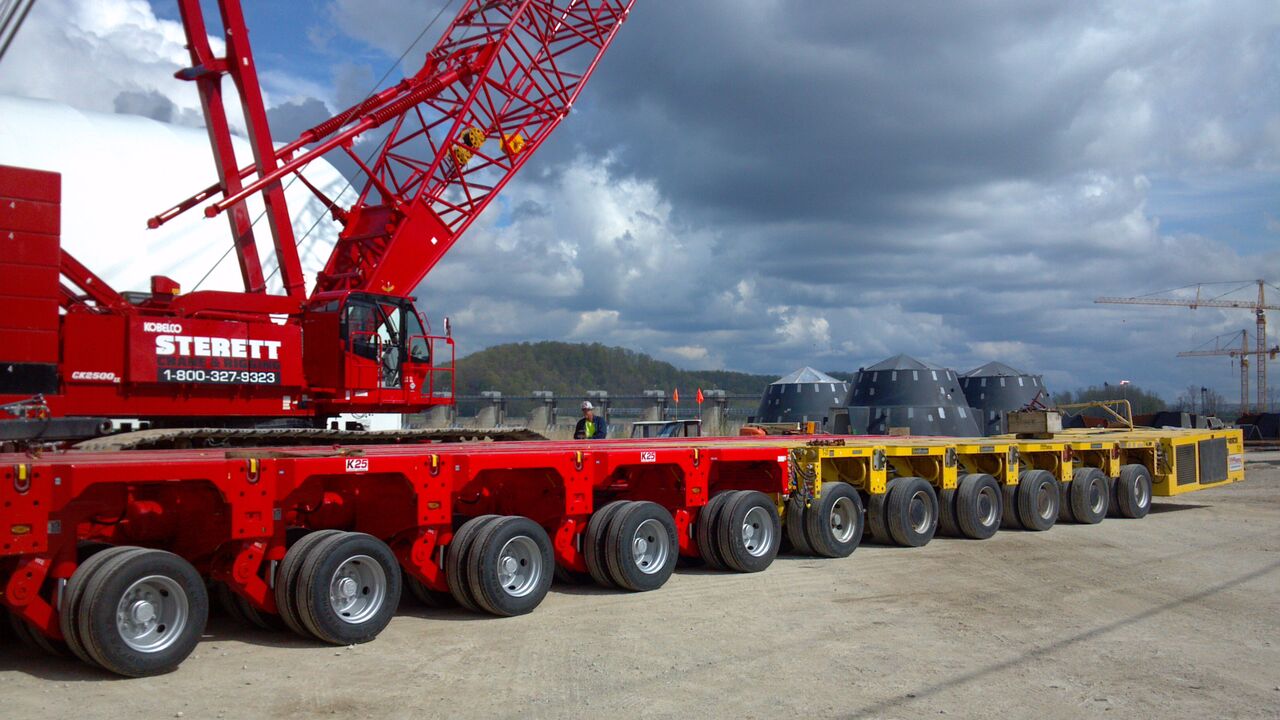

در آینده از همین وبلاگ نحوه ساخت فونداسیون توربین های بادی فراساحل کیسونی به توضحیات کامل نوشته شده و همچنین فیلم نحوه اجرای آن گذشته می شود.
حوضچه شناور (فلوتینگ داک) با توان بالابرى 2800 Ton براى بالا آوردن شناور هایى تا ظرفیت 8000DWT به طول 230متر و عرض 52 متر در سایت کشتى سازى وجود دارد.


Introduction to Marine Engineering, Second Edition,D.A.Taylor,Elsevier,1996
این کتاب دارای 383 صفحه می باشد درباره جزئیات کشتی و قسمت های آن نویسند شده است.
This Book Introduction to Marine Engineering, Second Edition,D.A.Taylor,Elsevier,1996
This file is Password
Password: CE-MS MS.c Bijan Mohammadi
All Text and change the color to use to download it
کلمه عبور/ Password دانلود/Download

کتاب مورد نظر با این عناوین می باشد./Book with this title
Chapter 1 Ships and machinery
Chapter 2 Diesel engines
Chapter 3 Steam turbines and gearing
Chapter 4 Boilers
Chapter 5 Feed systems
Chapter 6 Pumps and pumping systems
Chapter 7 Auxiliaries
Chapter 8 Fuel oils, lubricating oils and their treatment
Chapter 9 Refrigeration, air conditioning and ventilation
Chapter 10 Deck machinery and hull equipment
Chapter 11 Shafting and propellers
Chapter 12 Steering gear
Chapter 13 Fire fighting and safety
Chapter 14 Electrical equipment
Chapter 15 Instrumentation and control
Chapter 16 Engineering materials
Chapter 17 Watchkeeping and equipment operation

Bridge design and Evaluation LRFD and LRFR,Gongkang Fu,Wiley,2013
این کتاب دارای 438 صفحه می باشد در زمینه طراحی برزگراه و تقاطع پل ها طبق آیین نامه AASHTO می باشد وضریب ها اعمال شده و دارای مسئله کاربردی برای سازه پل می باشد.اولین چاپ این کتاب در سال 2003 چاپ شدبه عنوان کتابچه راهنما
This Book Bridge design and Evaluation LRFD and LRFR by Gongkang Fu,Wiley 2013
This file is Password
Password: CE-MS MS.c Bijan Mohammadi
All Text and change the color to use to download it
کلمه عبور/Password دانلود/Download

یک از ویژگی این کتاب می تواند از برای طراحی اسکله (Jetties) هم استفاده شود قسمت تکیه های عرشه و پایه پل
ضربه گیرهای زیر سری پل (نئوپرن) و انواع درز انبساط

نیروهای مکانیکی شامل بارهای افقی، عمودی و گشتاورهای وارده بر یک پل در ترکیب با تنشهای ناشی از انقباض و انبساط مصالح پل و خزش آنها موجب تغییر شکل در این سازه ها می شود.لذا برای کنترل این حرکات از ضربه گیرهای زیر سری پل (بالشتکهای نئوپرنی) استفاده می شود.
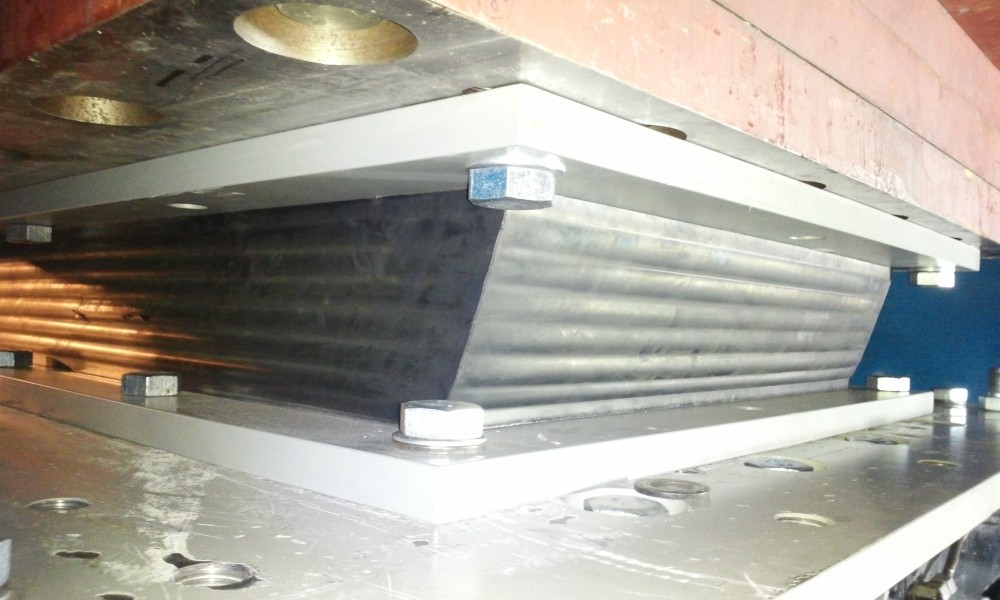

به زودی از همین وبلاگ فیلمی درباره آن ارایه می شود.این ضربه گیرها تلفیقی از فلز و لاستیک بوده و قطعات نگهدارنده ای هستند که در پلهای راه آهن،پلهای بتنی، پایه ساختمانها،فرودگاهها و سدها، اسکله ها که در معرض امواج بلند و خروشان قرار دارند استفاده می شوند. طراحی و تولید انواع ضربه گیرهای زیر سری پل بر اساس استانداردهای خاص و متناسب با میزان تحمل بار عمودی و افقی آنها و میزان جابجایی مجاز صورت می پذیرد.
یک زمانی به همین ضربه گیرهای پروژه های پل توی ایران به تاخیر خودن
Elastomeric Bearing & Expansion Joint

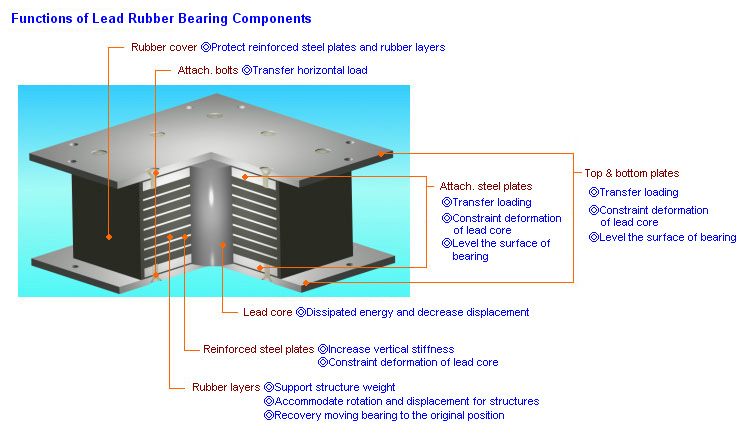
Bridge bearings are devices for transferring loads and movements from the deck to the substructure and foundations.The elastomeric bearing allows the deck to translate and rotate,,but also resists loads in the longitudinal,transverse and vertical directions. Loads are developed, and movement is accommodated by distorting the elastonmeric pad

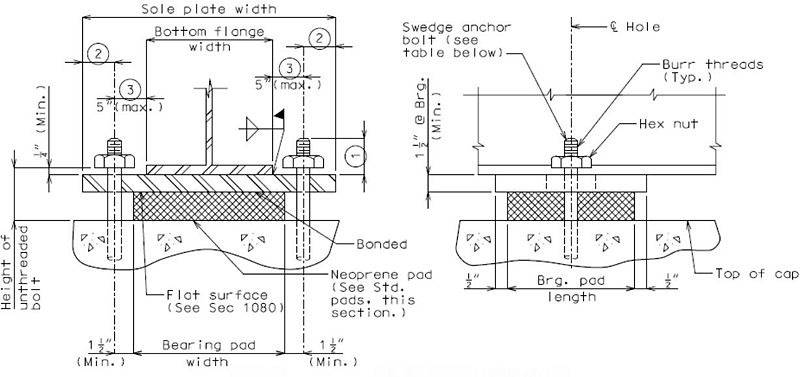
Bearings are arranged to allow the deck to expand and contract ,but retain the deck in its correct position on the substructure

 ,
,


کتاب مورد نظر با این عناوین می باشد./Book with this title
Chapter1 Introduction
Bridge Engineering and Highway Bridge Network
Types of Highway Bridges
Bridge Construction and Its Relation to Design
AASHTO Specifications and Design and Evaluation Methods
Goals for Bridge Design and Evaluation
Preliminary Design versus Detailed Design
Organization of This Book
References
Chapter 2 Requirements for Bridge Design and Evaluation
General Requirements
Limit States
Constructability
Safety
Serviceability
Inspect ability
Economy
Aesthetics
Summary
References
Problems
Loads, Load Effects, and Load Combinations
Chapter 3 Loads, Load Effects, and Load Combinations
Introduction
Permanent Loads
Transient Loads
Load Combinations
References
Problems
Chapter 4 Superstructure Design
Introduction
Highway Bridge Superstructure Systems
Primary Components of Highway Bridge Superstructure
Deck Systems
Deck-Supporting Systems
Design of Reinforced Concrete Deck Slabs
Design of Steel I Beams
Design of Prestressed Concrete I Beams
References
Problems
Chapter 5 Bearing Design
Introduction
Types of Bridge Bearing
Appropriate Selection of Bearings
Design of Elastomeric Bearings
References
Problems
Chapter 6 Substructure Design
Introduction
Piers
Abutments
Foundations
Design of Piers
Design of Abutments
References
Problems
Chapter 7 Highway Bridge Evaluation
Introduction
Inspection and Condition Rating
Load Rating
Fatigue Evaluation for Steel Components
References
Problems

Drilling Engineering,J.J.Azar & G.Robello Samuel,Pennwell,2007
این کتاب درباره مهندسی حفاری یک رشته چالش برانگیز و پیچیده نفت است. در زمینه فن آوری در دو ده گذشته این پیشرفت ها اجازه می دهد صنعت نفت در سراسر جهان از لحاظ اقتصادی و موفقیت بهره برداری حوزه نفت و گاز بهتر عمل شود.
دکتر آذر استاد ممتاز دانشگاه تولسا وباز نشسته مهندسی نفت است.او در دانشگاه در سال 1965 به عنوان استادیار در رشته مکانیک /مهندسی هوا فضا و در سال 1975 به پیشنهاد رشته مهندسی نفت و به عنوان استاد کامل مدیر دانشگاه تولسا انتخاب شد و در سال 1996 به عنوان ریئس گروه مهندسی نفت نایل گردد، در سال 2002 دکتر آذر رسما از دانشگاه بازنشسته شدبه دنبال فعالیت های خود در آموزش و مشاوره خدمت کرد. استاد آذر یک مدرس دانشگاه مشهور جهان و محقق در رشته مهندسی حفاری است .او در تمام شرکت های بزرگ نفتی و گازی در سراسر جهان کار کرده است دارای 4 کتاب درسی و بیش از 60 مقاله علمی و همچنین بیش از 100 سخنرانی در جلسات فنی و حرفه ای داشته است. او به پیشنهاد یکی از دانشگاه های دوحه قطر در سال 2004 دعوت شد و در آنجا سخنرانی کرد او به عنوان یک عضو مشورتی هیات تحریری دریایی می باشد بخشی از کتاب ایشان در زمینه حفاری دریایی می باشد.
دکتر Robrello مشاور ارشد فنی حفاری او دارای بیش از 18 سال تجربه در زمینه نفت و گاز یکی از مهارت های او برنامه ریزی ، طراحی ، برآورد هزینه ، نظارت حفاری و تکمیل عملیات، پرسنل و بررسی فنی ، نوآوری ایشان همچنین استاد دانشگاه و مدیر عامل شرکت هالی برتون و بالا تفگ حفاری در سال 1983تا 1992 به عنوان مهندس حفاری در یک شرکت نفت و گاز طبیعی مشغول به کار بوده است
This book Drilling Engineering,J.J.Azar & G.Robello Samuel,Pennwell,2007
Drilling engineering is a challenging discipline in the oil patch. It goes beyond what is found in textbooks
The technological advances in the past two decades have been very significant. These advances have
allowed the oil industry worldwide to economically and successfully exploit oil and gas fields that may have not been possible before
Dr. J. J. Azar , PhD, PE, SPE, NAE, is a professor emeritus of Petroleum Engineering at the University of Tulsa. He joined the university in 1965 as an assistant professor in Mechanical/ Aerospace Engineering, and was promoted to associate professor in 1969. In 1975, he joined the Petroleum EngineeringDepartment as full professor and Director of the University of Tulsa Drilling Research Projects, a joint oil and gas industry research program. In 1996, he stepped down from the directorship to devote full time to teaching and writing. He served as acting chairman of the Petroleum Engineering Department in 2001. Dr.Azar officially retired from the University May 31, 2002, to pursue his own activities in teaching and consulting. Professor Azar is a world-renowned lecturer and researcher in drilling engineering. As a director of drilling research, he is credited with building one of the most comprehensive and top drilling engineering curricula in the Department of Petroleum Engineering at the University of Tulsa, worldwide. He has led his graduate students to pioneering research work in areas of cuttings transport in directional well drilling, drilling fluids hydraulics, drill bit, and drill string dynamics. He is closely associated and worked with all major oil and gas companies across the globe. His contributions to the advancement of drilling technology through teaching, research, and publications are notable. He is the author and/or coauthor of four textbooks and more than 60 publications in refereed technical journals. He has given more than 100 presentations at technical meetings and professional functions. He has been invited as keynote speaker at
several technical conferences. Professor Azar was a participant speaker at the Advances in Drilling Technologies” workshop organized by the U.S. National Research Council and the National Academy of Sciences. In 2004, he was invited by the University of Chicago to be session leader and group facilitator on Materials science conference held in Doha, Qatar. He has served as a member of the SPE Education and Professionalism Technical Committee, SPE Student Chapter adviser, SPE Career Guidance and Student Development Committee, Technical reviewer, Committee Chairman/Member on the “SPE Distinguished Achievement Award for Petroleum Engineering Faculty,” Committee Chairman/Member on the “AIME Mineral Industry Education Award” and Member of Editorial Advisory Board of Offshore
Dr. Azar received the 1998 SPE Drilling Engineering Award and the 1997 SPE Distinguished Achievement Award for Petroleum Engineering Faculty. He was elected as SPE Distinguished Member for the year 2004. He was inducted into the U.S. National Academy of Engineering in Washington, D.C, in 2004. He is a registered professional engineer and a member of SPE. His areas of interest in teaching and research include: well bore fluids hydraulics, wellbore mechanics,drill bit mechanics, drill string mechanics, and well control mechanics in application to vertical, directional, horizontal, multilateral, coiled tubing, under-balanced, and slim hole drilling
Dr. G. Robello Samuel is a Senior Technical Advisor (Drilling) in the Drilling, Evaluation, and Digital Solutions division of Halliburton, where he has been since 1998. He has more than 18 years of experience in domestic and international oil/gas drilling and completion operations, management, consulting and teaching. His skills include well planning, design, cost estimates, supervision of drilling and completion operations, personnel and technical review, project management, and creative establishment of project relationships through partnering and
Innovation. Presently he is a technical and engineering lead for well planning engineering application suite for drilling, completions, and well services operations. Also he is an adjunct professor at the University of
Houston teaching advanced drilling and complex well architecture courses
He has authored or coauthored more than 50 conference and journal papers. He has given several graduate seminars at various universities. Dr. Samuel has been the recipient of numerous awards including the “CEO for A Day (Halliburton)” and “Top Gun (Drilling)” awards. He has also worked at Oil and Natural Gas Corporation, India from 1983 to 1992 as a drilling engineer. He is
Presently serving as a Review Chairman on the Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE) Drilling and Completions Editorial Review Committee, American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Journal of Energy Resources Technology and as co-chairman of SPE Multilateral Technical Interest Group. His other professional experience includes being on the 2006–2008 drilling committee of SPE.
He holds BS and MS (Mechanical Engineering) degrees from University of Madurai, Madurai and College of Engineering Guindy, Anna University (Chennai), MS and PhD (Petroleum Engineering) degrees from the University of Tulsa. He is a member of ASME and SPE
His areas of research include wellbore fluids hydraulics, tubular design, thermal and flow phenomena and their effect on loading of wellbore tubulars, drilling and well cost optimization and downhole tool hydrodynamics
Dr. G. Robello Samuel is a Senior Technical Advisor (Drilling) in the Drilling, Evaluation, and Digital Solutions division of Halliburton, where he has been since 1998. He has more than 18 years of experience in domestic and international oil/gas drilling and completion operations, management, consulting and teaching. His skills include well planning, design, cost estimates, supervision of drilling and completion operations, personnel and technical review, project management, and creative establishment of project relationships through partnering and
Innovation. Presently he is a technical and engineering lead for well planning engineering application suite for drilling, completions, and well services operations. Also he is an adjunct professor at the University of Houston teaching advanced drilling and complex well architecture courses He has authored or coauthored more than 50 conference and journal papers. He has given several graduate seminars at various universities. Dr. Samuel has been the recipient of numerous awards including the “CEO for A Day (Halliburton)” and “Top Gun (Drilling)” awards. He has also worked at Oil and Natural Gas Corporation, India from 1983 to 1992 as a drilling engineer. He is Presently serving as a Review Chairman on the Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE) Drilling and Completions Editorial Review Committee, American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Journal of Energy Resources Technology and as co-chairman of SPE Multilateral Technical Interest Group. His other professional experience includes being on the 2006–2008 drilling committee of SPE.He holds BS and MS (Mechanical Engineering) degrees from University of Madurai, Madurai and College of Engineering Guindy, Anna University (Chennai), MS and PhD (Petroleum Engineering) degrees from the University of Tulsa. He is a member of ASME and SPEHis areas of research include wellbore fluids hydraulics, tubular design, thermal and flow phenomena and their effect on loading of wellbore tubulars, drilling and well cost optimization and downhole tool hydrodynamics
This file is password
Password :CE-MS MS.c Bijan Mohammadi
All Text and change the color to use to download it
Download/دانلود کلمه عبور/Password

Chapter 1 Rotary Drilling for Oil and Natural Gas
Introduction
The Process of Rotary Drilling
Rotary Drilling Rigs
Rig Selection
Rotary Drilling Systems
Mud System Evaluation
Rotary System
Well Control System
Data Acquisition and Monitoring System
Special Systems for Offshore Drilling
Supplementary Problems
Nomenclature
Chapter 2 Drilling Fluids
Characteristics of a Drilling Fluid
Drilling-Fluid Selection
Classification of Drilling Fluids
Water-Based Drilling-Mud Contaminants
Drilling-Mud Properties, Field Tests, and Control
Alkalinity (Mf, Pf, Pm, Mm, P1, P2)
Mud Rheology
Drilling-Mud Additives
Supplementary Problems
Nomenclature
Chapter 3 Fluid Flow and Associated Pressures in the Rotary Rig Circulating System
Introduction
Mechanical Energy and Pressure Balance
Pressure Drop across the Bit Nozzles (Jets)
Friction Pressure Losses in the Rotary Rig Circulating System
Friction Pressure Losses in Pipes and Annuli—Laminar Flow
Friction Pressure Losses in Pipes and Annuli—Turbulent Flow
Equivalent Newtonian Viscosity
Turbulent Pipe Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids
Turbulent Annular Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluids
Annular Friction Pressure Losses Due to Pipe Movement
Supplementary Problems
Nomenclature
References
Chapter 4 Drill Bit Hydraulics
Introduction
Pump Pressure Requirement in Rotary Drilling
Hydraulic Power Requirement
Flow Exponent (α)
Maximum Drill Bit Hydraulic Horsepower Criterion
Maximum Jet Impact Force Criterion
Supplementary Problems
Nomenclature
References
Chapter 5 Transport of Drilled Cuttings
Introduction
Factors that Affect the Transport of Drilled Cuttings
Cuttings Transport in Vertical Well Drilling
Cuttings Transport in Directional Well Drilling
Empirical Correlations for Cuttings Transport in High-Angle Wells (θ > 50°)
Supplementary Problems
Nomenclature
References
Chapter 6 Prevention and Control Mechanics of Well Blowouts
Introduction
Kick Causes
Kick Detection
Kick Prevention
Fundamentals of Well Control
Well Control System
Principles of Well Control
Commonly Used Well Control Methods
Non conventional Kick Situations
Supplementary Problems
Nomenclature
References
Chapter 7 Directional and Horizontal Well Drilling
Directional Well Drilling
Horizontal Well Drilling
Tortuosity
Supplementary Problems
Nomenclature
References
Chapter 8 Drill Bit Mechanics
Introduction
Bit Selection
Types of Drill Bits
Classification of Roller Cone Drill Bits
Drill Bit Operating Parameters
Grading of Dull Drill Bits
Classification of Drag Drill Bits
Rock Mechanics
Performance Mechanics of Drag Drill Bits
Supplementary Problems
Nomenclature
References
Chapter 9 Drill String Design
Definition and Components
Design Criteria
Buckling of the Drill String
Drill String Fatigue
Dril String Vibration
BHA Design for Directional Drilling
Deviation Tools
Supplementary Problems
Nomenclature
References
Chapter 10 Drilling Problems and Solutions
Introduction
Pipe Sticking
Loss of Circulation
Hole Deviation
Drill Pipe Failures
Borehole Instability
Mud Contamination
Producing-Formation Damage
Hole Cleaning
Hydrogen Sulfide–Bearing Zones and Shallow Gas
Equipment- and Personnel-Related Problems
Supplementary Problems
Nomenclature
References
Chapter 11Casing and Cementing Design
Drilling the Pay Zone: Selecting the Interval and the Initial Design
Initial Completion Design
Casing Design
Cementing
Supplementary Problems
Nomenclature
References
Chapter 12 Well Planning in Drilling Engineering
Introduction
Objectives
Information Needed for Effective Well Planning
Responsibilities of the Drilling Engineer
Considerations in Well Planning
The Drilling Program
Post-Well Analysis
Well Cost Estimation
Learning Curve
Cost Control in Well Drilling
Time Value of Money
Price Elasticity
Supplementary Problems
Nomenclature
Nonlinear Finite Element Methods, Peter Wriggers,Springer, 2008*
Nonlinear Finite Element Methods, Peter Wriggers,Springer2008
This file is password
Password :CE-MS MS.c Bijan Mohammadi
All Text and change the color to use to download it
Password/کلمه عبور دانلود/ Download

Chapter 1 Introduction
Chapter 2 Nonlinear Phenomena
* Geometrical Nonlinearity
Large Displacements of a Rigid Beam
Large Displacements of an Elastic System
Bifurcation Problem
Snap-Through Problem
Physical Nonlinearity
Nonlinearity Due to Boundary Conditions
Chapter 3 Basic Equations of Continuum Mechanics
* Kinematics
Motion and Deformation Gradient
Strain Measures
Transformation of Vectors and Tensors
Time Derivatives
Balance Equations
Balance of Mass
Balance of Linear and Angular Momentum
First Law of Thermodynamics
Introduction of Different Stress Tensors
Balance Equations with Respect to Initial Configuration
Time Derivatives of Stress Tensors
Constitutive Equations
Elastic Material
Elasto-Plastic Material Laws
Visco-Elastic and Visco-Plastic Material Behaviou
Incremental Form of the Material Equations
Weak Form of Equilibrium, Variational Principles
Weak Form of Linear Momentum in the Initial Configuration
Weak Form of Linear Momentum in the Current Configuration
Variational Functionals
Linearizations
Linearization of Kinematical Quantities
Linearization of Constitutive Equations
Linearization of the Variational Formulatio
Chapter 4 Spatial Discretization Techniques
* General Isoparametric Concept
One-Dimensional Interpolations
Two-Dimensional Interpolations
Three-Dimensional Interpolation
Discretization of the Weak Form
FE-Formulation of the Weak Form in Initial Configuration
Linearization of the Weak Form in the Initial Configuration
FE-Formulation of the Weak Form in the Current Configuration
Linearization of the Weak Form in the Current Configuration
Deformation Dependent Loads
Chapter 5 Solution Methods for Time Independent Problems
*Solution of Nonlinear Systems of Equations
Newton-Raphson Method
Modified Newton Scheme
Quasi-Newton Method
Damped Newton Method, Line-Search
Path-Following or Arc-Length Method
Solvers for Linear Systems of Equations
Direct Solvers
Iterative Solution Methods
Parallel Equation Solver
Examples Related to Algorithms and Equation Solvers
Rubber Block
Solid with an Inclusion
Elasto-Plastic Plate with Hole
Problems Solved on Parallel Computers
General Observations
Problems, Which Occur when Running Actual Simulations
Chapter 6 Solution Methods for Time Dependent Problems
Chapter 7 Stability Problems
Chapter 8 Adaptive Methods
Chapter 9 Special Structural Elements
Chapter 10 Special Finite Elements for Continua
Chapter 11 Contact Problems
Chapter 12 Automation of the Finite Element Method by J. Korelc