
دنیای مهندسی سازه های دریایی
Offshore Structures
دنیای مهندسی سازه های دریایی
Offshore StructuresFrontiers in Offshore Geotechnics II,Susan Gourvenec and David White,CRC Press,2010
این کتاب درباره سرحدهای ژئوتکنیک فراساحلی می باشد، که دارای 939 صفحه است مجموعه ای از مقالات ارسالی به دانشگاه غربی استرالیا می باشد که توسط نویسندگان جمع آوری شده است. با این عناوین
Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics II,Susan Gourvenec and David White,CRC Press,2010
The titles
This file is password
Password: CE-MS MS.c Bijan Mohammadi
All text and change the color to use to download it
دانلود / Download کلمه عبور/Password

1 Keynotes
A systematic approach to offshore engineering for multiple-project developments in geohazardous areas
Recommended best practice for geotechnical site characterisation of cohesive offshore sediments
Gulf of Guinea deepwater sediments: Geotechnical properties, design issues and installation experiences
Geotechnics for subsea pipelines
Axial and lateral pile design in carbonate soils
New frontiers for centrifuge modelling in offshore geotechnics
Risk and reliability on the frontier of offshore geotechnics
2 Geohazards and gas hydrates
Neotectonic deformation of northwestern Australia: Implications for oil and gas development
Deepwater Angola part I: Geohazard mitigation
Deepwater Angola part II: Geotechnical challenges
Shallow gas hazard linked to worldwide delta environments
Analysis of submarine flow slides in fine silty sand
Hydrate dissociation around oil exploration infrastructure
An investigation of past mass movement events in the West Nile Delta
Deformation of seabed due to exploitation of methane hydrate reservoir
3 In situ site characterisation and pore pressure measurement
A site investigation strategy to obtain fast-track shear strength design parameters in deep water soils
Enhancement of the ball penetrometer test with pore pressure measurements
Laboratory free falling penetrometer test into clay
Offshore sediment overpressures: Overview of mechanisms, measurement and modeling
Angolan deep water soil conditions: GIS technology development for sediment characterization
Strength measurement in very soft upper seabed sediments
CPT in polar snow – preliminary observations
Parametric study of a free-falling penetrometer in clay-like soils
The future of deep water site investigation: Seabed drilling technology?
Mini T-bar testing at shallow penetration
Piezometer installation in deep water Norwegian Sea
Luva deep water site investigation programme and findings
Investigations into novel shallow penetrometers for fine-grained soils
Seabed drilling vs surface drilling – a comparison
4 Soil characterisation and modelling
Rheological behaviour of soft clays
A three-dimensional finite element study of the direct simple shear test
Repeated loading and unloading of the seabed
A new interpretation of the simple shear test
Physical modelling of the crushing behaviour of granular materials
New evidence for the origin and behaviour of deep ocean ‘crusts’
Soil unit weight estimated from CPTu in offshore soils
Strain rate dependent simple shear behaviour of deep water sediments in offshore Angola
Simplified calibration procedure for a high-cycle accumulation model based on cyclic triaxial tests on 22 sands
Understanding cyclic loading behavior of soil for offshore applications
5 Shallow foundations
Observations of shallow skirted foundations under transient and sustained uplift
Numerical study of grillage foundations on sand under combined VHM loading
The vertical bearing capacity of grillage foundations in sand
Behaviour of skirted footings on sand overlying clay
Numerical study of piping limits for suction installation of offshore skirted foundations and anchors in layered sand
Shallow foundation performance in a calcareous sand
A numerical study of the vertical bearing capacity of skirted foundations
The effect of torsion on the sliding resistance of rectangular foundations
Foundation design challenges of the MCR-A skirted gravity platform
Constructing breakwater with prefabricated caissons on soft clay
6 Piled foundations
Simplified analysis of laterally loaded pile groups
Behavior of piles under combined lateral and axial loading
Investigations on the behavior of large diameter piles under cyclic lateral loading
BP Clair phase 1 – Pile driveability and capacity in extremely hard till
Photoelastic investigation into plugging of open ended piles
Soil-pile interaction during extrusion of an initially deformed pile
BP Clair phase 1 – Geotechnical assurance of driven piled foundations in extremely hard till
Pile driving experiences in Persian Gulf calcareous sands
FLAC3D analysis on soil moving through piles
Cyclic loading of barrettes in soft calcareous rock using Osterberg cells
Shaft capacity of drilled and grouted piles in calcareous sandstone
Numerical analysis of mudmat contribution to capacity of piled offshore platforms
Simplified numerical model for analysis of offshore piles under cyclic lateral loading
Centrifuge modelling of rapid load tests with piles in silt and sand
Field measurements on monopile Dolphins
Behaviour of driven tubular steel piles in calcarenite for a marine jetty in Fujairah, United Arab Emirates
CPT-Based design method for axial capacity of offshore piles in clays
7 Foundations for renewable energy
Evaluation of pile capacity approaches with respect to piles for wind energy foundations in the North Sea
Installation of suction caissons for offshore renewable energy structures
Lateral behaviour of large diameter monopiles at Sheringham Shoal Wind Farm
Centrifuge modelling of offshore monopile foundation
Gravity based foundations for the Rødsand 2 offshore wind farm, Denmark
Geotechnics for developing offshore renewable energy in the US
Engineering issues for fixed offshore wind turbines on Lake Michigan Mid Lake Plateau, USA
Centrifuge model tests on piled footings in clay for offshore wind turbines
Design of monopile foundations in sand for offshore windfarms
Experimental evaluation of backfill in scour holes around offshore monopoles
An investigation of the use of a bearing plate to enhance the lateral capacity of monopile foundations
Optimizing site investigations and pile design for wind farms using geostatistical methods: A case study
Towards the FE prediction of permanent deformations of offshore wind power plant foundations using a high-cycle accumulation model
Cyclic accumulation effects at foundations for offshore wind turbines
Study on soil-structure interaction of suction caisson by large-scale model tests
8 Jack-up units
Simplified VH equations for foundation punch-through sand into clay
Characterisation of undrained shear strength using statistical methods
Centrifuge modelling of spudcan deep penetration in multi-layered soils
A probabilistic approach to the prediction of spudcan penetration of jack-up units
An assessment of jackup spudcan extraction
3D FE analysis of the installation process of spudcan foundations
Undrained bearing capacity of deeply embedded foundations under general loading
9 Anchoring systems
Trajectory prediction for drag embedment anchors under out of plane loading
Setup following keying of plate anchors assessed through centrifuge tests in kaolin clay
Seismically-induced displacements of a suction caisson in soft clay
SEPLA keying prediction method based on full-scale offshore tests
Set-up of suction piles in deep water Gulf of Guinea clays
Centrifuge testing of suction piles in deep water Nigeria clay – Effect of stiffeners and set-up time
Numerical FEM and laboratory study of the bearing capacity factor Nc for plate anchors
Caisson capacity in clay: VHM resistance envelope – Part 2: VHM envelope equation and design procedures
Installation and in-place assessment of drag anchors in carbonate soil
Caisson capacity in clay: VHM resistance envelope – Part 1: 3D FEM numerical study
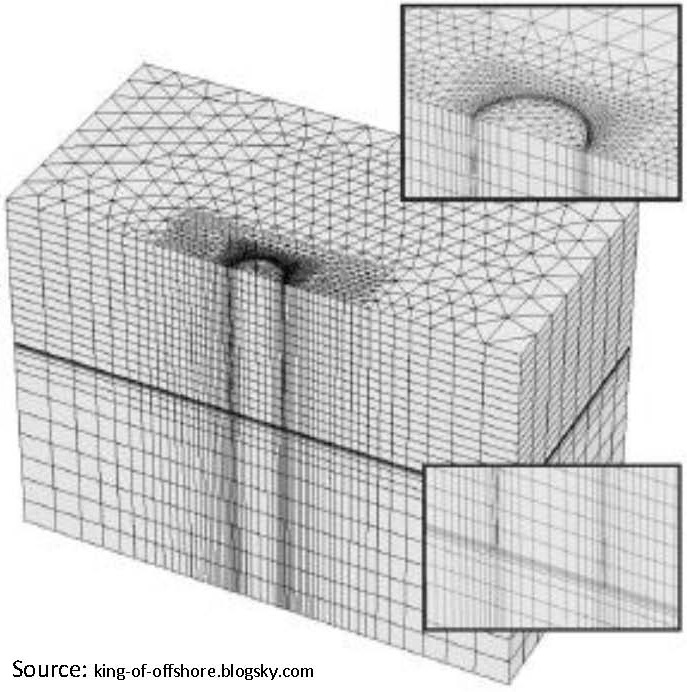
Numerical investigation of the behaviour of suction caissons in structured clays
Cyclic moment loading of suction caissons in sand
10 Pipelines and risers
Multidirectional analysis of pipeline-soil interaction in clay
Geotechnical challenges for deep water pipeline design – SAFEBUCK JIP
Large deformation finite element analysis of vertical penetration of pipelines in seabed
Implementation of geotechnical techniques in the analysis of pipeline response
Lateral soil resistance to an untrenched pipeline under the action of ocean currents
Vertical cyclic testing of model steel catenary riser at large scale
Kupe gas project pipeline – optimisation of discrete rock berm design shore approach
Model test studies on soil restraint to pipelines buried in sand
Pipe-soil interaction on clay with a variable shear strength profile
Sweeping behaviour of shallowly-embedded pipeline during cyclic lateral movement
Advanced nonlinear hysteretic seabed model for dynamic fatigue analysis of steel catenary risers
Mobilization distance in uplift resistance modeling of pipelines
Theoretical, numerical and field studies of offshore pipeline sleeper crossings
Observations of pipe-soil response from the first deep water deployment of the SMARTPIPE®
11 Trenching, ploughing, excavation and burial
Influence of object geometry on penetration into the seabed
Investigation into the effect of forecutters on plough performance
State-of-the-art jet trenching analysis in stiff clays
Numerical modelling of soil around offshore pipeline plough shares
Anchor–chain–rock fill–soil interaction: Evolution of design methods
Development of a jet trenching model in sand
12 Design and risk
Structural factors affecting the system capacity of jacket pile foundations
The new API Recommended Practice for Geotechnical Engineering: RP 2GEO
Comparison of ISO 19901-2 and API RP 2A seismic design criteria for a site in the Caspian Sea, Turkmenistan

فیلم آموزشی آزمایش نفوذ مخروط در بستر دریا توسط کشتی /Educational film on the seabed Cone Penetration Test by ship
فیلم آموزشی آزمایش نفوذ مخروط در بستر دریا توسط کشتی
Educational film on the seabed Cone Penetration Test by ship

دستگاه نفوذ مخروطی Cone Penetration Test ( CPT) یکی از کاراترین دستگاه های آزمایشهای برجا
In situ testing مطالعات ژئوتکنیک می باشد.

ثبت نتایج بصورت پیوسته در عمق بستر دریا، امکان ثبت فشار آب منفذی بصورت پیوسته، امکان تشخیص لایه های با ضخامت بیشتر از 5 سانتیمتر از خاکهای روانگرا ( لنزهای ماسه ای) تکرار پذیر بودن نتایج آزمایش (Repeatability) استاندارد بودن نحوه انجام آزمایش، کاهش دست خوردگی خاک و سرعت انجام آزمایش، از مهمترین ویژگی های دستگاه CPT می باشد.


فیلم نحوه آزمایش نفوذ مخروط با ماشین/Video of cone penetration test with car
این فیلم نحوه آزمایش نفوذ مخروط را نشان می دهد.
This is Video of cone penetration test
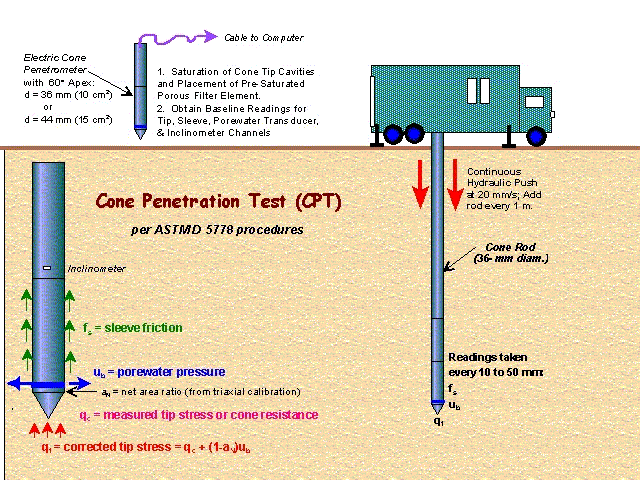
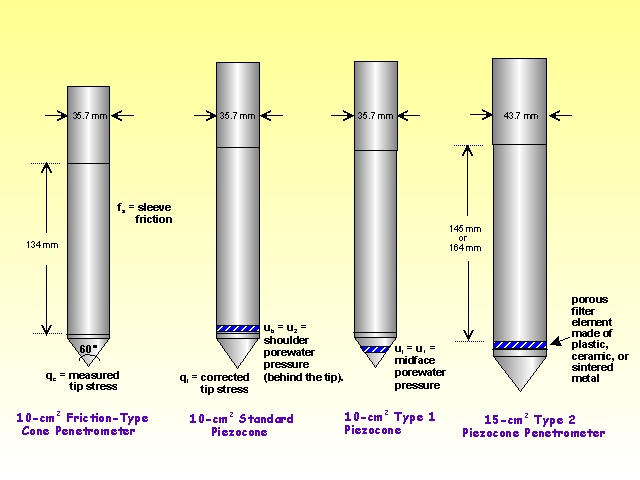

The cone penetration or cone penetrometer test (CPT) is a method used to determine the geotechnical engineering properties of soils and delineating soil stratigraphy. It was initially developed in the 1950s at the Dutch Laboratory for Soil Mechanics in Delft to investigate soft soils. Based on this history it has also been called the "Dutch cone test". Today, the CPT is one of the most used and accepted in soil methods for soil investigation worldwide.
The test method consists of pushing an instrumented cone, with the tip facing down, into the ground at a controlled rate (controlled between 1.5 -2.5 cm/s accepted). The resolution of the CPT in delineating stratigraphic layers is related to the size of the cone tip, with typical cone tips having a cross-sectional area of either 10 or 15 cm², corresponding to diameters of 3.6 and 4.4 cm. A very early ultra-miniature 1 cm² subtraction penetrometer was developed and used on a US mobile ballistic missile launch system (MGM-134 Midgetman) soil/structure design program in 1984 at the Earth Technology Corporation of Long Beach, CA
Cone Penetration Testing (CPT) is used to identify subsurface conditions in the upper 100 ft of the subsurface. The USGS CPT uses a 23-ton truck to push a “cone” into the ground. The weight of the truck is partially supported by both the tip of the cone and the sleeve of the cone. The “tip resistance” is determined by the force required to push the tip of the cone and the “sleeve friction” is determined by the force required to push the sleeve through the soil. The “friction ratio” is the ratio between sleeve friction and tip resistance, measured as a percentage. Soil type and thereby resistance to liquefaction can be inferred from these measurements

فیلم نحوه آزمایش نفوذ مخروط/Video of cone penetration test
آزمایش نفوذ مخروط CPT
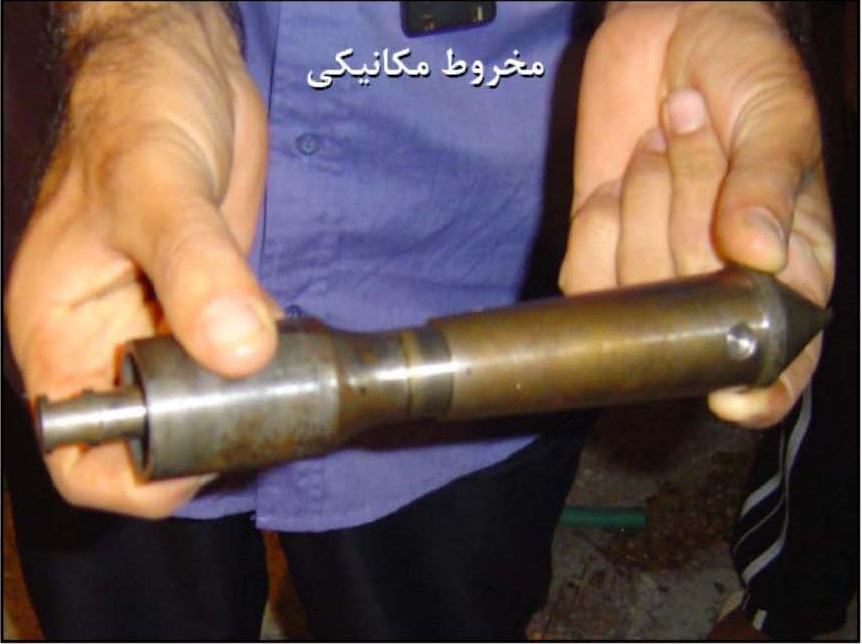

این آزمایش بجای آزمایش نفوذ استاندارد بخصوص برای رسها ولای های نرم و رسوبات ماسه ای ریز تا متوسط، بطور وسیعی مورد استفاده قرار گرفته است. این آزمایش تناسب چندانی با رسوبات شنی یا رسوبات چسبنده سفت و سخت ندارد.
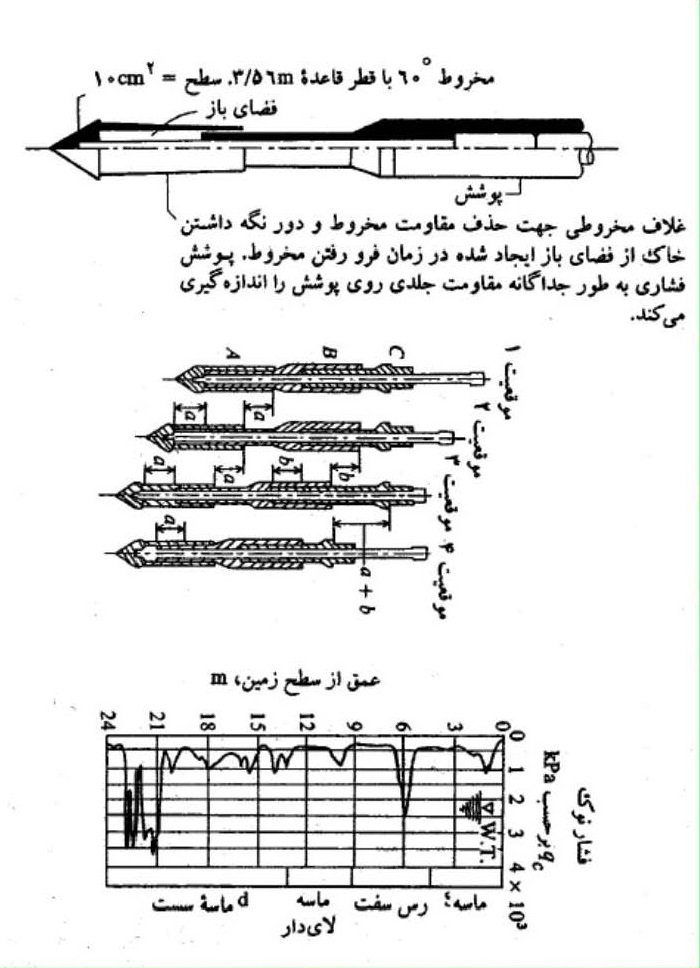
این آزمایش شامل فشردن مخروطی استاندارد به داخل زمین با سرعت 10 تا 20 میلیمتر بر ثانیه و ثبت مقاومت مربوطه می باشد. اطلاعات ثبت شده معمولا مقاومت جانبی مخروط، مقاومت اتکائی و عمق می باشد.

چنانچه خاک دارای لایه بندی باشد این آزمایش را می توان همراه
با حفاری انجام داد. در
این حالت گمانه تا لایه سست حفاری
شده و آزمایش انجام می شود، سپس گمانه تا لایه بعدی
حفر گردیده و آزمایش مجددا انجام می شود و اینکار تا عمق
و لایه های مورد نظر ادامه می یابد
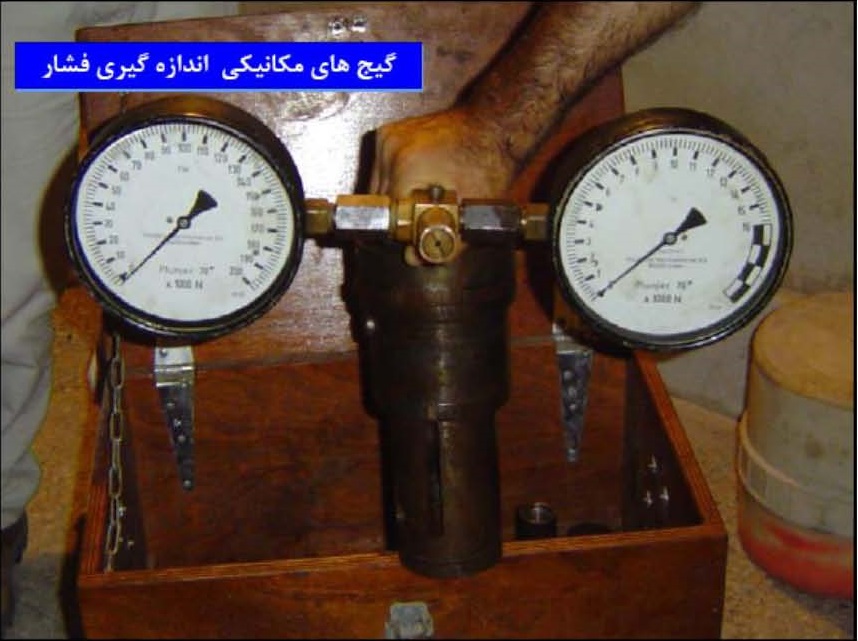

مقاومت اندازه گیری شده نوک و اصطکاک جداری به صورت زیر برای محاسبه نسبت اصطکاک بکار برده می شود:
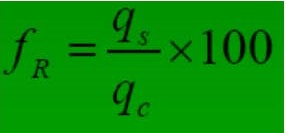
از نسبت اصطکاک برای طبقه بندی خاک استفاده می شود. نسبت اصطکاک را می توان با استفاده از رابطه تجربی و تقریبی زیر برای تخمین حساسیت خاک بکار گرفت.
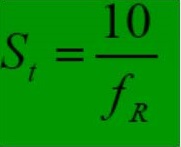

Geotechnical Engineering Princies of soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering V.N.S. Murthy
این کتاب درباره مکانیک خاک و مهندسی پی می باشد
This book is about the Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering

