دنیای مهندسی سازه های دریایی
Offshore Structures
دنیای مهندسی سازه های دریایی
Offshore StructuresMono Piles Foundation installation/نصب شاسی توربین های بادی فراساحل
Mono Piles Foundation installation
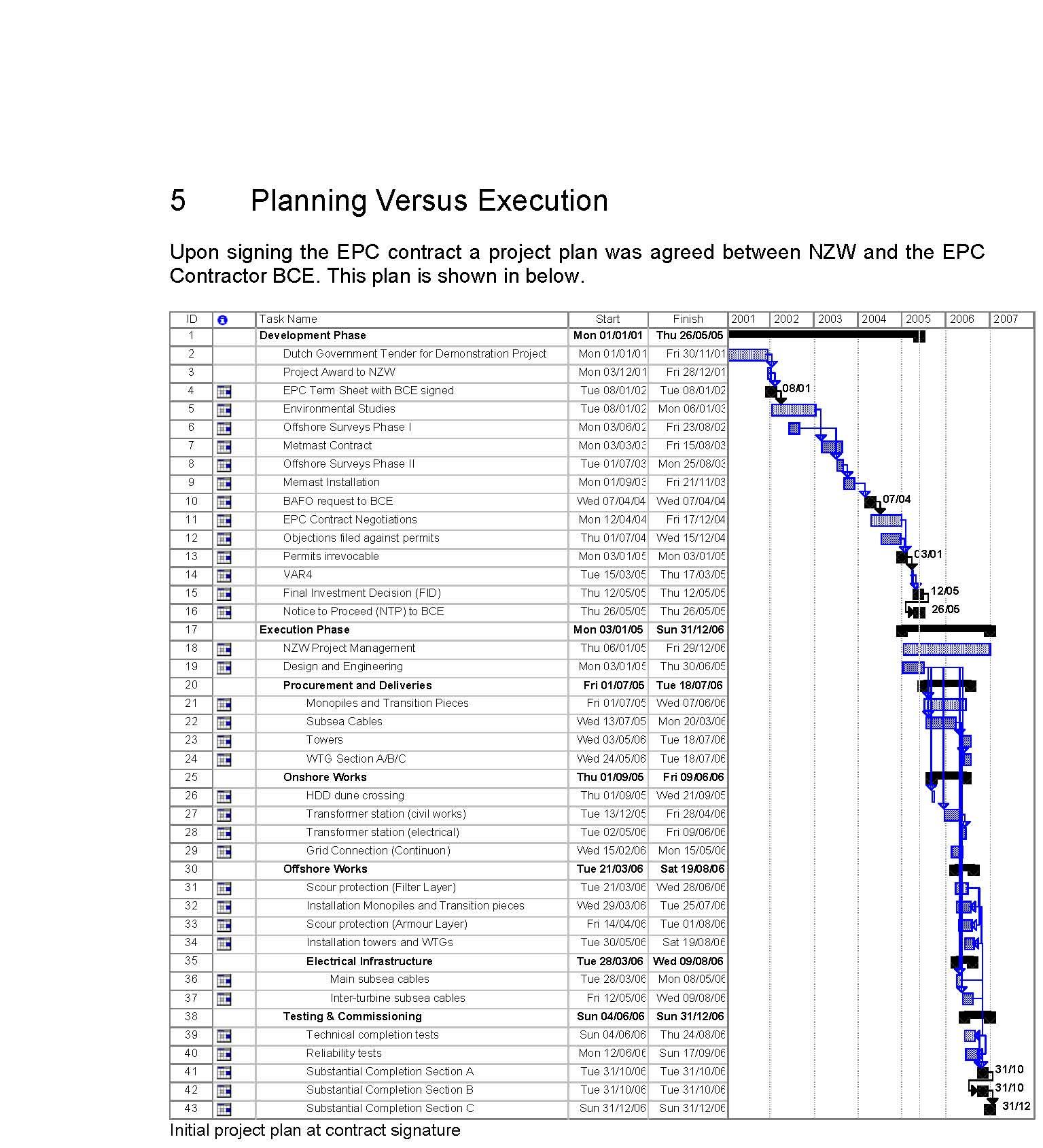
Depending on the foundation type, the installation vessel and strategy may differ.
Currently, approximately 90% of offshore wind turbines are installed on monopiles and the remainder are installed on jackets, tripods or gravity-based support structures.
There are also a few demonstration floating turbines, which have no bottom-fixed
foundations.
Mono piles
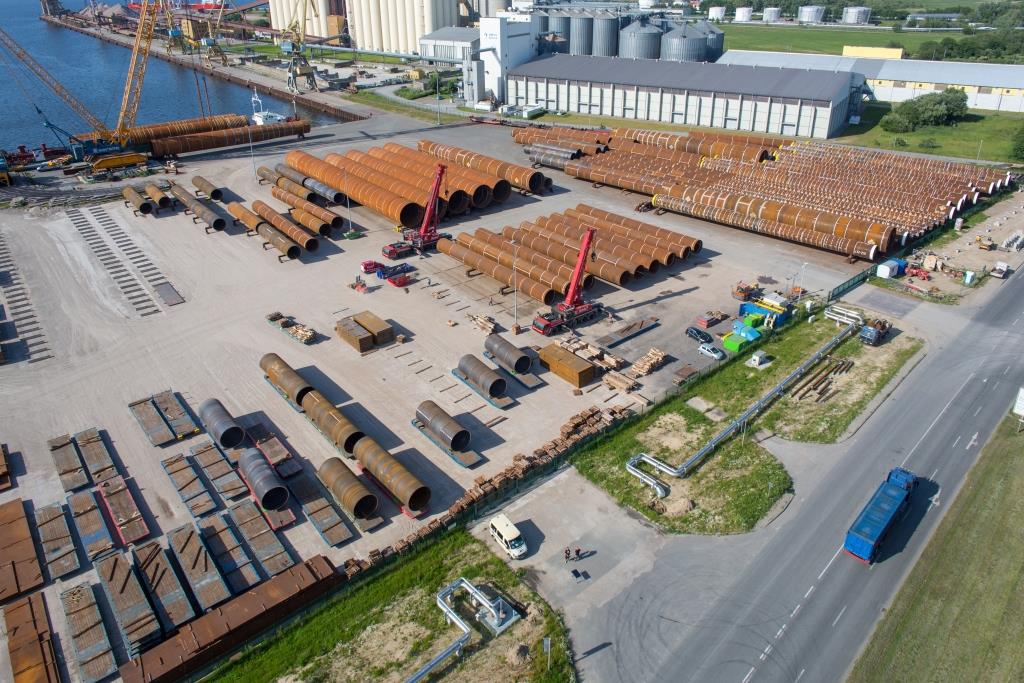

The the foundation pile or Mono pile (MP) support structure is a relatively simple design by which the tower is supported by the mono pile, either directly or through a Transition piece or (Transition Platform) (TP). One of the main advantages of the mono pile foundation is the easy application for a large number of wind turbines. A large number of piles can be transported to the building site by the installation vessel itself or by a transportation barge. The next step is the installation of the scour protection (static scour protection), although it is possible to install scour protection after pile installation (dynamic scour protection). The foundation used is a steel monopile, 45m long on average with a diameter of 4,6m and a wall thickness of 40 to 60mm. Its weight is approx. 230 tons. These piles were made at Bladt industries in Denmark.

The transition piece is lifted and placed on the top of the monopile and then the space between the monopile and the transition piece (about 10e20 cm thick) is
grouted. The top of the transition piece is used as the work platform and the sides
are used for boat landing and ladder placement The mono pile continues down into the seabad.
Monopiles are large hollow steel or concrete tubes, whose thickness and diameter vary
based on the turbine size, soil condition , water depth and hydrodynamic loads on the monopile portion: wave, current, and ice loads, seismic loads.The effects of wave and current kinematics on the loading of a monopile tower can be
calculated via the Morison equation for slender members
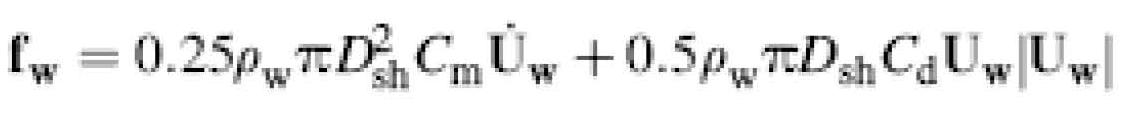
wind-generated, near surface currents, and subsurface currents generated by tidal motion, storm surges, and atmospheric pressure Variations
Before installation of a monopile, a layer of scour protection should be applied to avoid seabed erosion around the monopile. This first scour protection layer is made by rock dumping around the monopile position. When the first layer of scour protection is made, monopiles are lifted from the installation vessel and then positioned on the seabed.
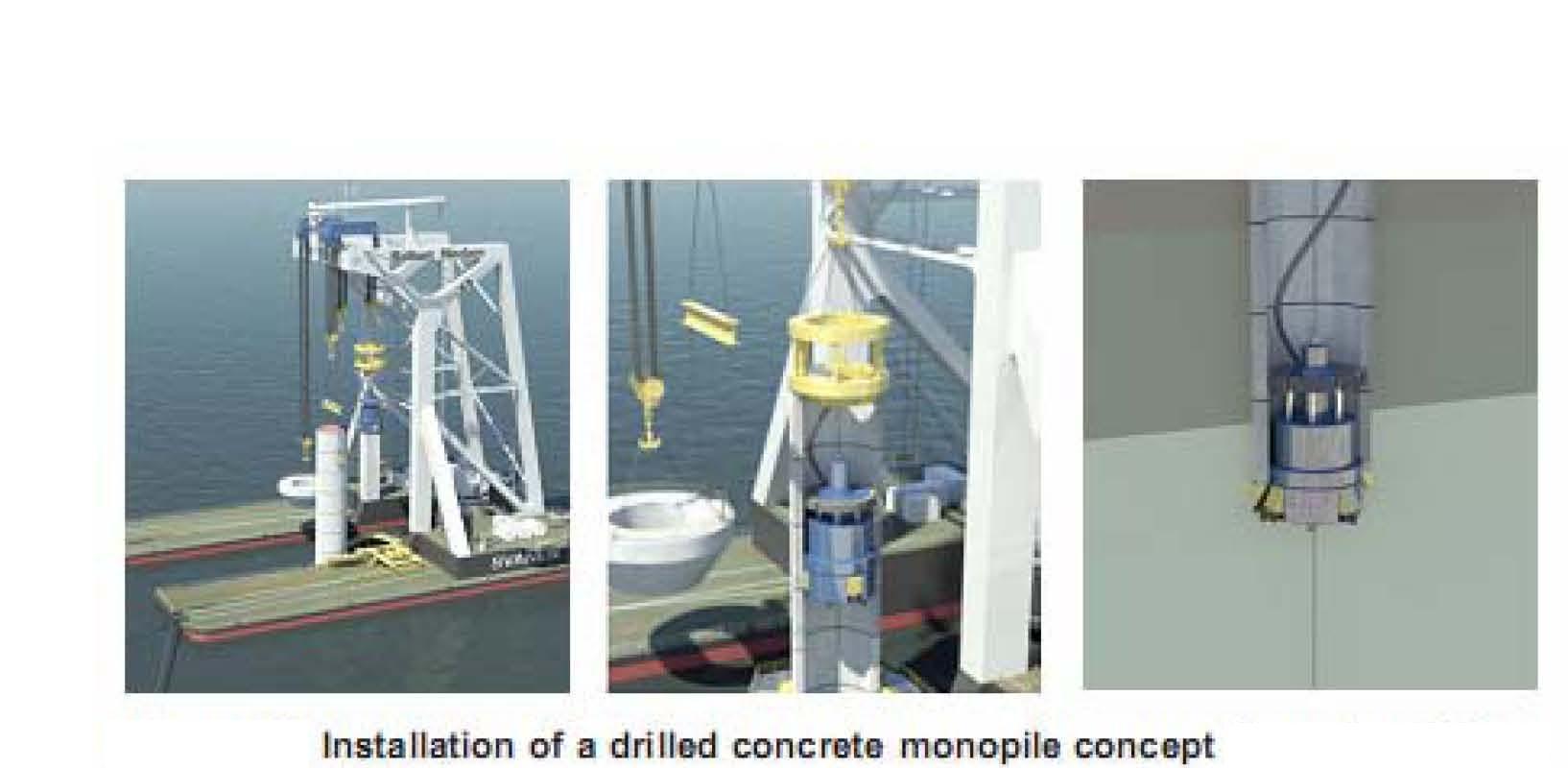
Common installation methods of monopiles are pile driving using a hydraulic hammer or pile drilling .

On average it takes about one or two days to install a monopile using these methods. If pile driving using a hydraulic hammer is chosen,depending on the seabed condition and water depth, it takes about 2000 to 3000 hammer hits to drive the monopile into the ground. During the pile driving or drilling,the piling depth is continuously monitored to make sure the monopile is placed into the correct depth.
The installation sequence of the pile starts with lifting it into position by a large crane or heavy lift vessel. The pile will be lifted from a floating position, afterwards the bulk heads will be removed and then the open ended pile can be aligned into position. This will be done by an alignment tool at a certain distance above the sea level, as can be seen in Figure. The pile will penetrate into the seabed due to its own weight, depending on the soil conditions. To drive the pile into the ground, a hydraulic hammer is lifted onto the pile, or the pile can be drilled in case of very hard soil.
Around the foundation a layer of rocks was placed to provide scour protection. As seawater flows around the monopile it creates turbulence which erodes the seabed sand directly around the monopile (this is the actual scour process) and so endangers the
stability of the foundation. The scour protection prevents the sand from being eroded away. In total about 50.000 tons of stone have been installed on the seabed around the monopiles (see also Figure below).
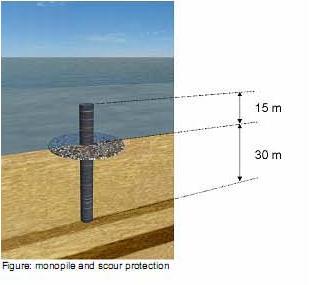
In figure a schematic overview is given on the major parts of an offshore windmill
At the bottom of the wind turbine is the foundation pile or monopile (MP
This is a simple steel tube that is hammered into the seabed. Because it is hammered, it cannot be guaranteed that it is perfectly vertical. Also the top of the pile gets damaged in this process
Indicated in yellow is the Transition Piece (TP). Typical characteristics are as follows: the lower 6m of this 25m high structure slides over the top of the monopile. Jacks are used to align the TP vertically to correct the MP skewness. Then the space between the TP and MP is grouted to fix the connection.
Furthermore the top of the TP offers a nice flange for the tower to be bolted o
After that the tower is installed on top of the TP. The Rotor Nacelle Assembly (RNA) is installed on top of the tower, sometimes in one go, and sometimes first the nacelle is installed and then each
blade independently afterwards.
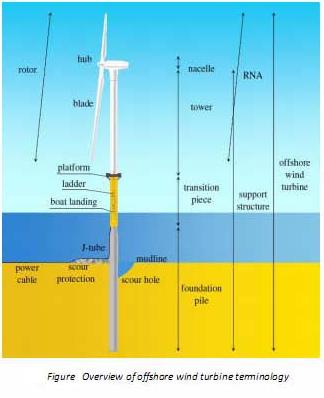
The suction pile can also be a support structure in combination with a monopole on top of it . The suction pile is relatively short in relation to the diameter, and therefore called pile, but the
diameter can be larger compared to the length and in that case it is called a suction can or suction anchor . The main principle behind the suction anchor is the pressure difference, which is createdby pumping the water out of the pile or can while it is placed upside down on the seabed. The pressure difference is the main driving force to drive the pile into the seabed, and therefore this support structure is less suitable for shallow waters. Furthermore, the tension capacities and bending moment capacities might be lower compared to a pile foundation. The suction pile is not taken into account any further.

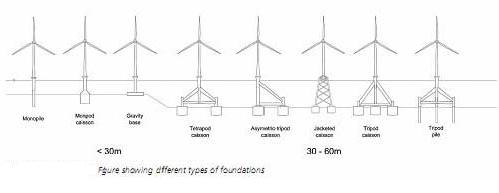
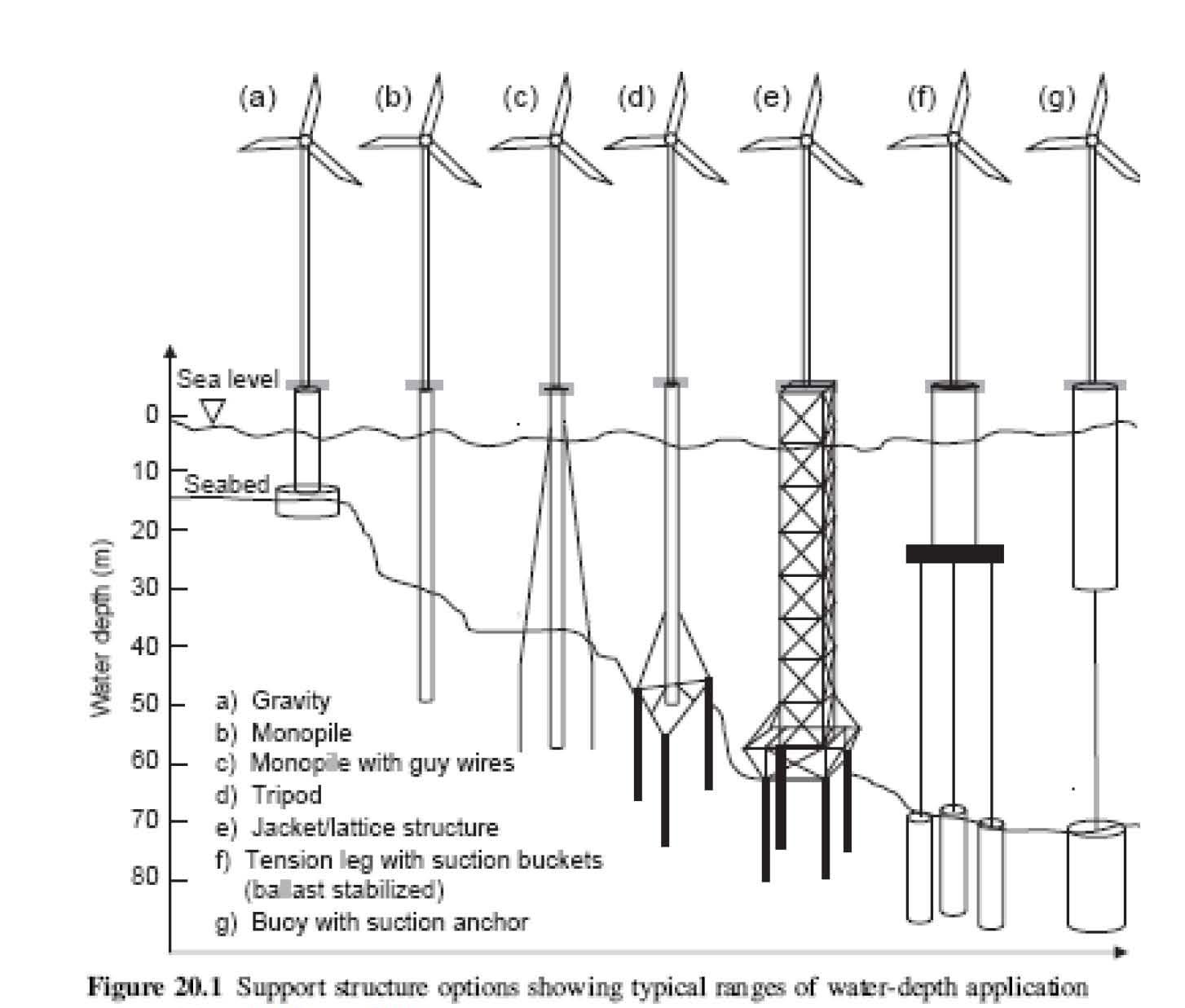
Monopiles are typically used in shallow water depths, but may become too flexible for water depths of between w30 and 40 m, in which case monopiles fitted with guy wires, or alternatively tripod and jacket/lattice structures,are considered as economical alternatives. For greater depths, time-consuming
installation and the effect of soil degradation, which occurs around the pile shaft at seabed level, make monopile foundation solutions prohibitive
امیدوارم در فیلم های بعدی توضیح بیشتری درباره این سازه و نحوه چیدمان حلقه ، جوش پودری ، تست جوش و دیگر مراحل این سازه بنویسم .
هدف از نمایش این فیلم نحوه انتقال سازه به محل پروژه بود انتقال این سازه به دو روش است سوار کردن روی بارج یا شناور کردن این سازه و کشیدن ان توسط یدک است همه اینها بستگی به طول سازه دارد.
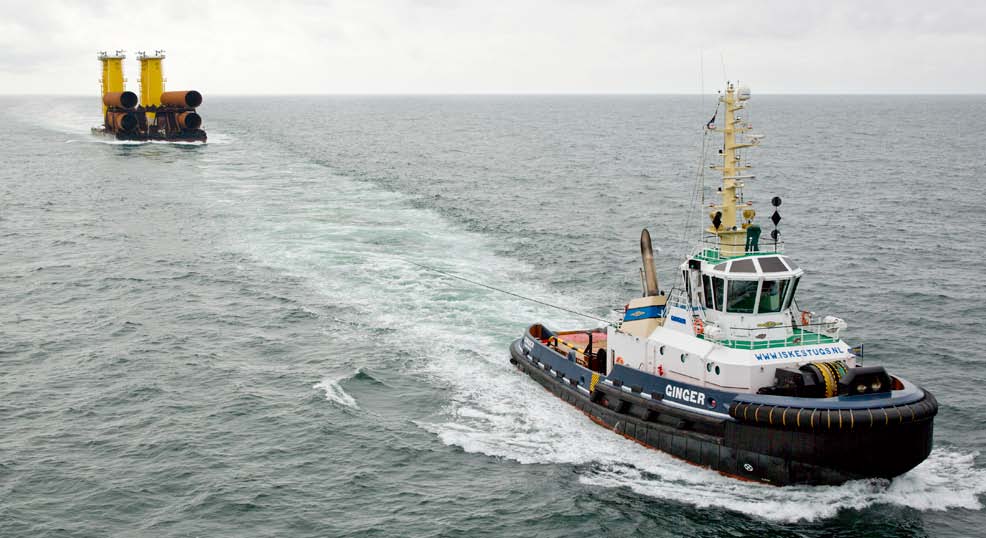





این پروژه ها توسط سرمایه گذاری مشترک چندین کشور اورپایی انجام می شود که برای مراحل انجام هر کاری یا قسمتی از آن در کشورهایشان سرمایه گذاری شده است و امروزی برای کم هزینه کردن این پروژه ها در حال مطالعه هستند تا بتواند هم تجهیزات کم هزینه استفاده شود هم برنامه زمان بندی آن را کاهش دهند.در قسمت های بعدی درباره کارخانه ساخت شاسی توربین های فراساحل بیشتر خواهم نوشت