
دنیای مهندسی سازه های دریایی
Offshore Structures
دنیای مهندسی سازه های دریایی
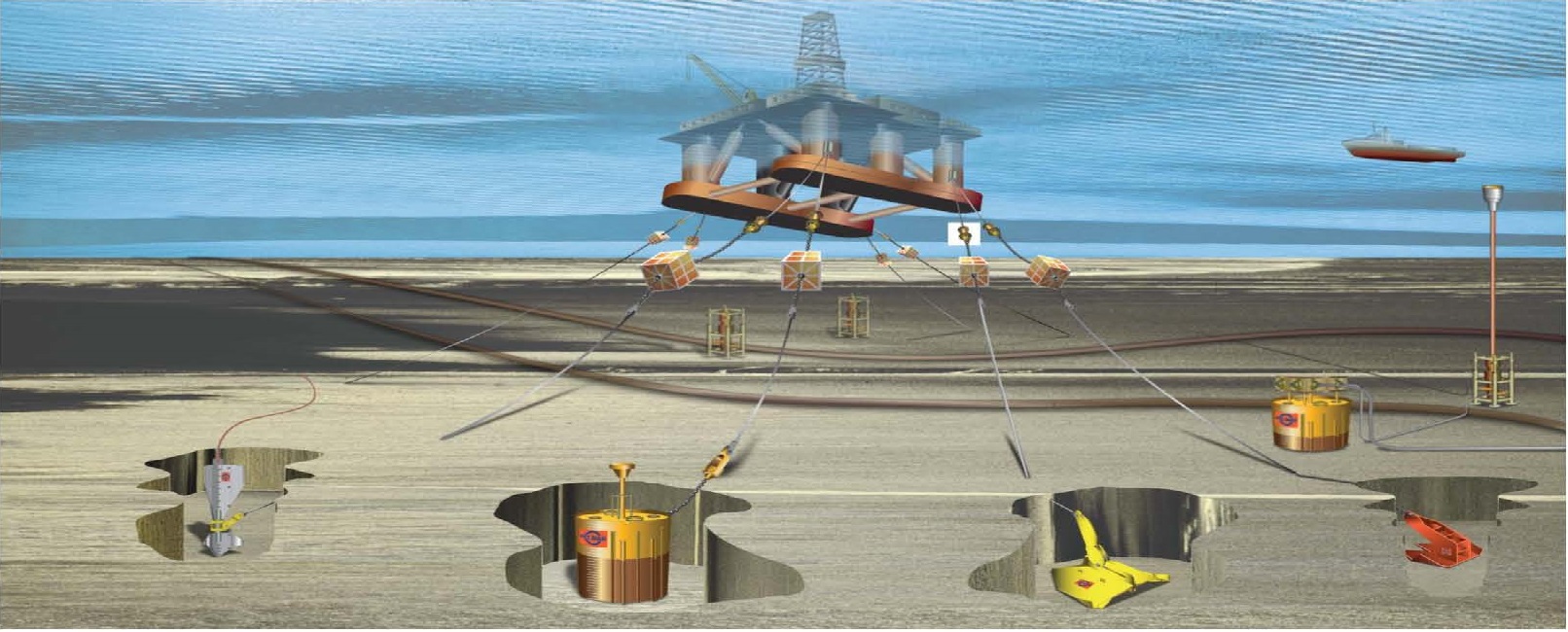
Offshore Structuresنصب منیفولد بر روی شمع مکشی /Installed of manifold on the suction pile
این انیمیشن طریقه نصب منیفولد (سازه چند ظرفیتی) را روی شمع مکشی نشان می دهد.
This animation show manifold on the suction pile
بعد از نصب شمع مکشی حال نوبت سازه منیفولدمی باشد
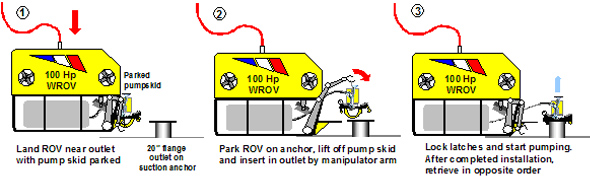


برای اینکه دقت نصب بالا باشد از میله های راهنما روی شمع مکشی استفاده می شود این میله ها 2 تا هستند یکی بزرگ دیگری کوچک و توسط چشم دریا سازه به طرف میله ها هدایت می شوند.

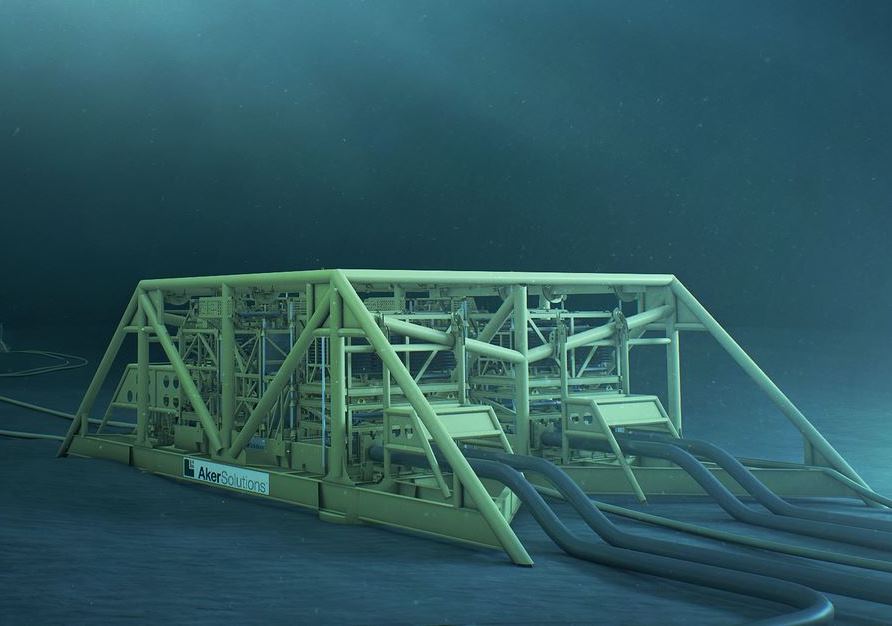
تجهیزات زیر دریا عبارتند از:
Subsea production equipment
Subsea equipment
*Trees
*Manifolds
*Spools
*Flying leads
*Subsea distribution system (SDC)
*Umbilical (chemicals, hydraulics, Fibre optics)
*Flow line
* HIPPS
*SSIV
*Export pipeline
*Controls, SCMs, Automations
*Electrical heating

قبلا در همین وبلاگ درباره منیفولد توضیح داده شده است.
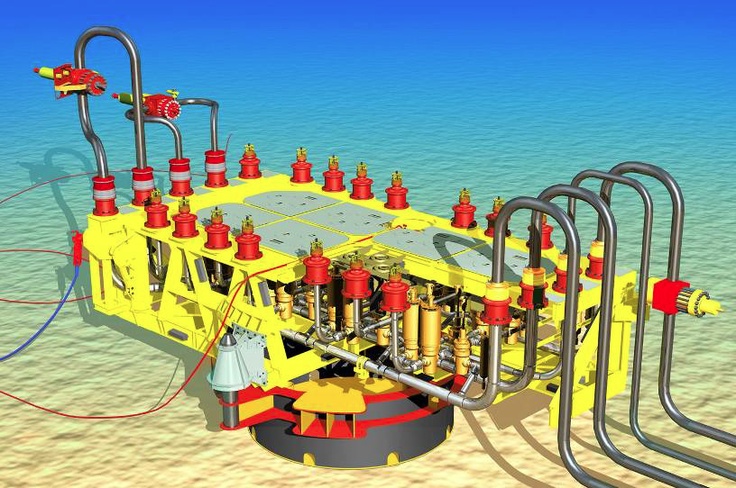
A production manifold is a subsea structure containing valves and pipework designed to commingle and direct produced fluids from multiple wells into one or more flowlines. Our cluster style production manifolds play a key role in well testing, isolation, sampling, and allocation management.

Typical subsea Manifold

Subsea Manifold

*It is a gravity-bassed seafloor structure the consists of an arrangement of valves, pipes, and fittings.
*It serves as a central gathering point for production from subsea wells
*redirects the combined flow to the host facility
* A subsea manifold may not be needed for some subsea designs
*For example, developments where the individual production Trees are directly tied into the host facility
* A manifold arrangement can be any shape, but normally is rectangular or circular
*May be either a stand-alone structure or integrated into a well template
*The manifold may be anchored to the seafloor with piles or skirts that penetrate the mud line.
*Size is dictated by the number of wells
*valves
*chokes for flow control
*control system equipment
*header can include lines for water or chemical injection, gas lift and well conrol
*Also the pattern how the subsea wells are integrated into the system.
*The likely range of dimensions for a subsea manifold would be 24m (diameter for circular design), standing up to 9 m above the seafloor

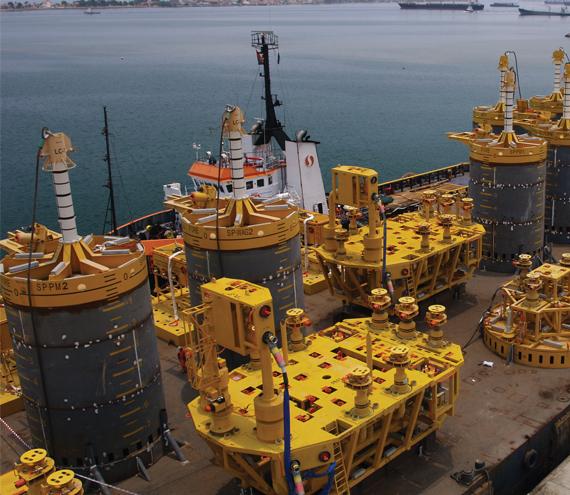
یکی از گرانترین سازه زیر دریا منیفولد است شیرهای آن از طلایی 21 عیار می باشد با ضریب امنیتی بالا این سازه طراحی شده در عمق های 800 تا این زمان مورد استفاده قرار گرفته است
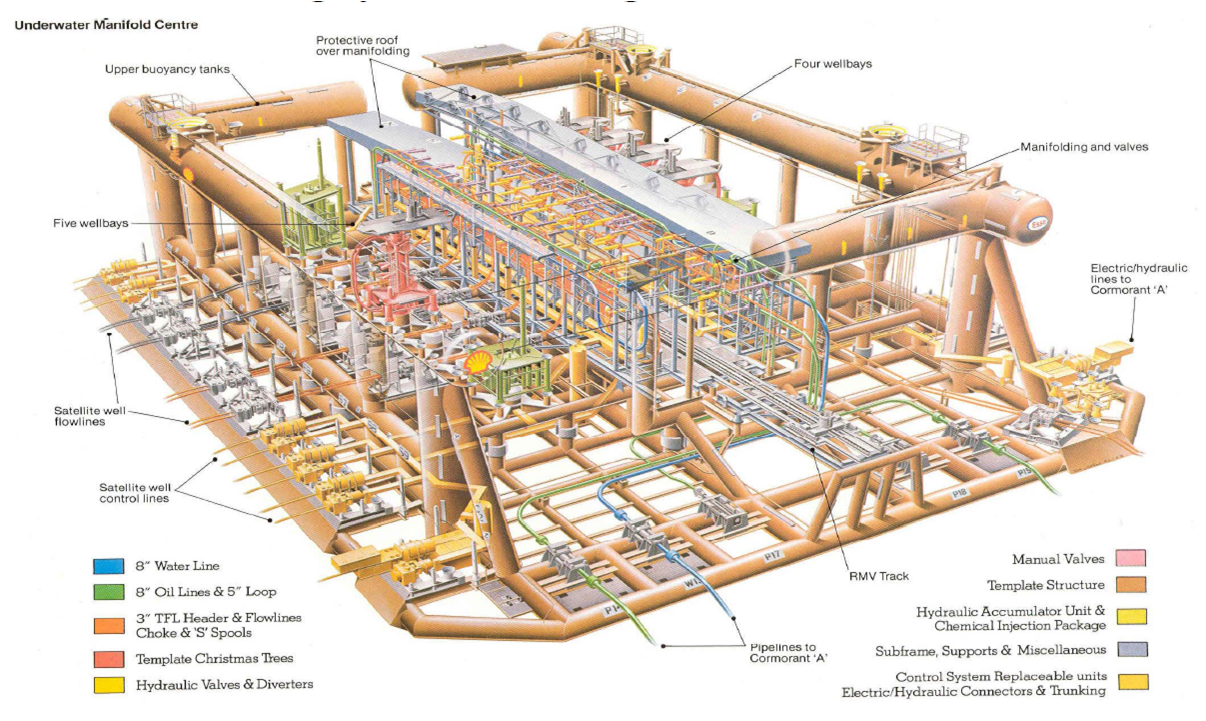
چیده مان تجهیزات و آرایش آنها از سر چاه شروع می شود

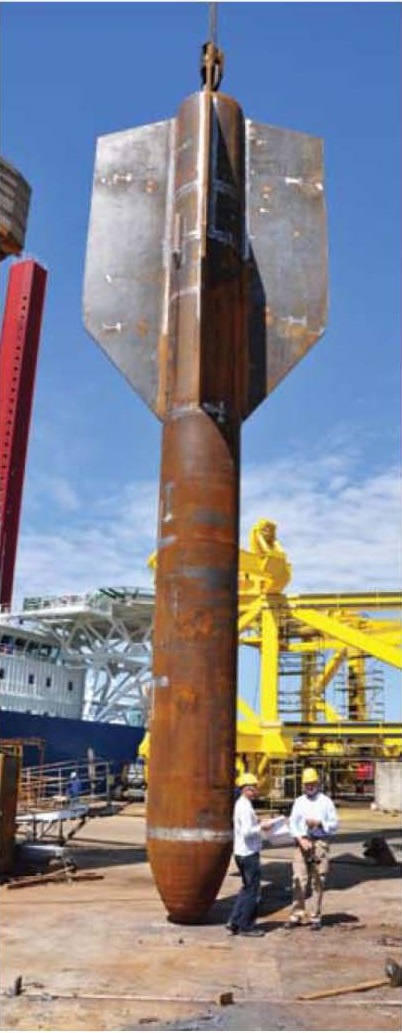
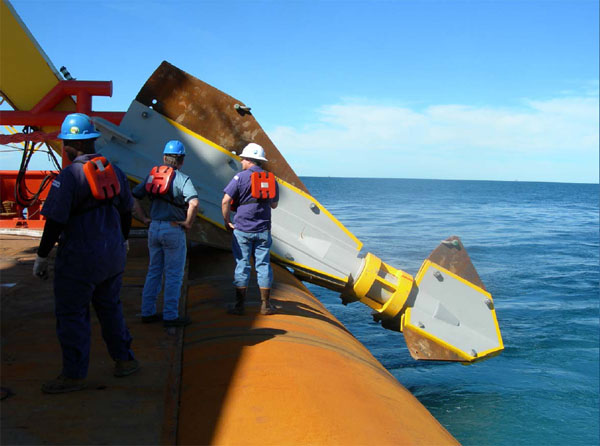
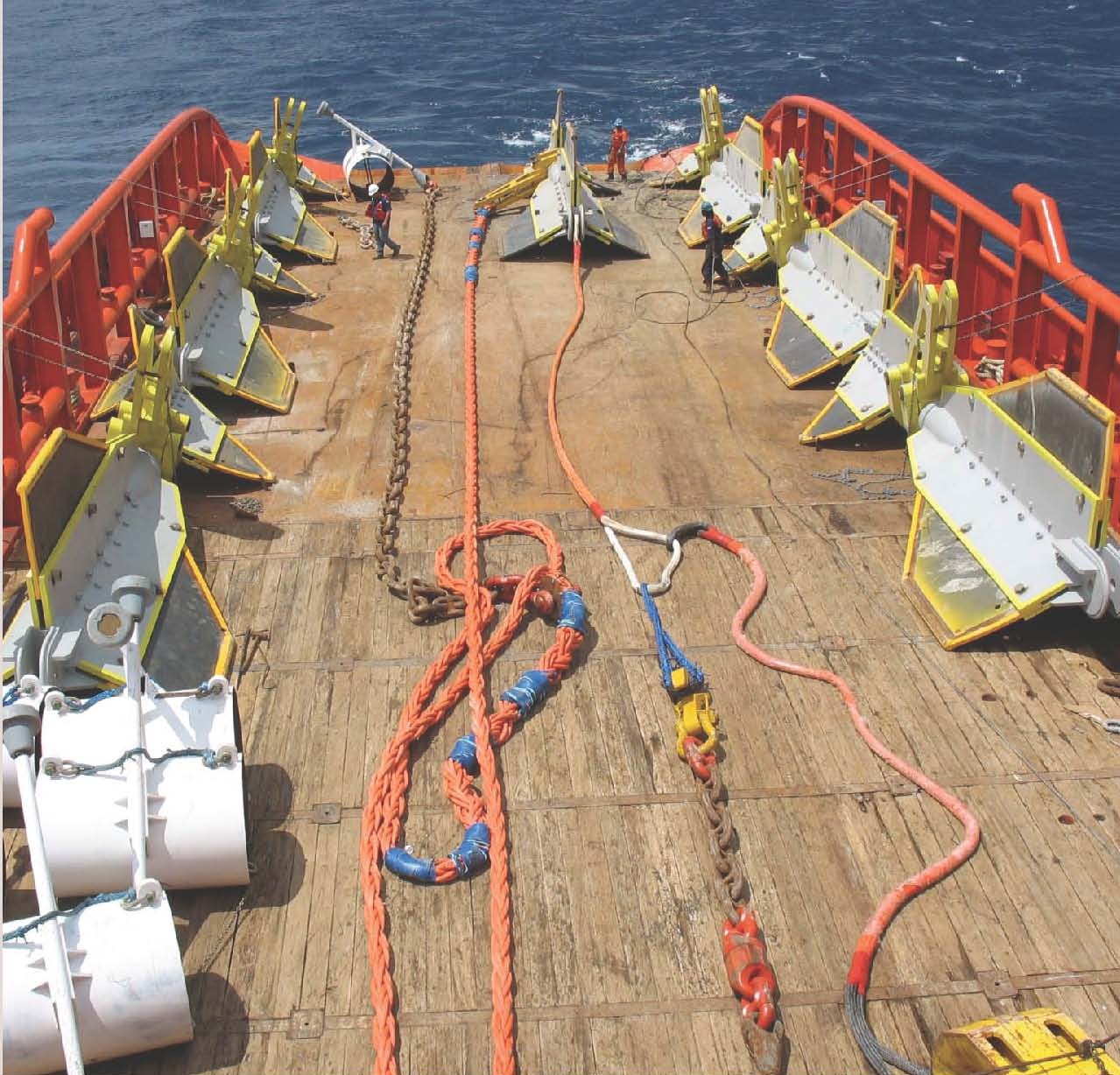
Runnig of the suction anchore/اجرای لنگر مکشی
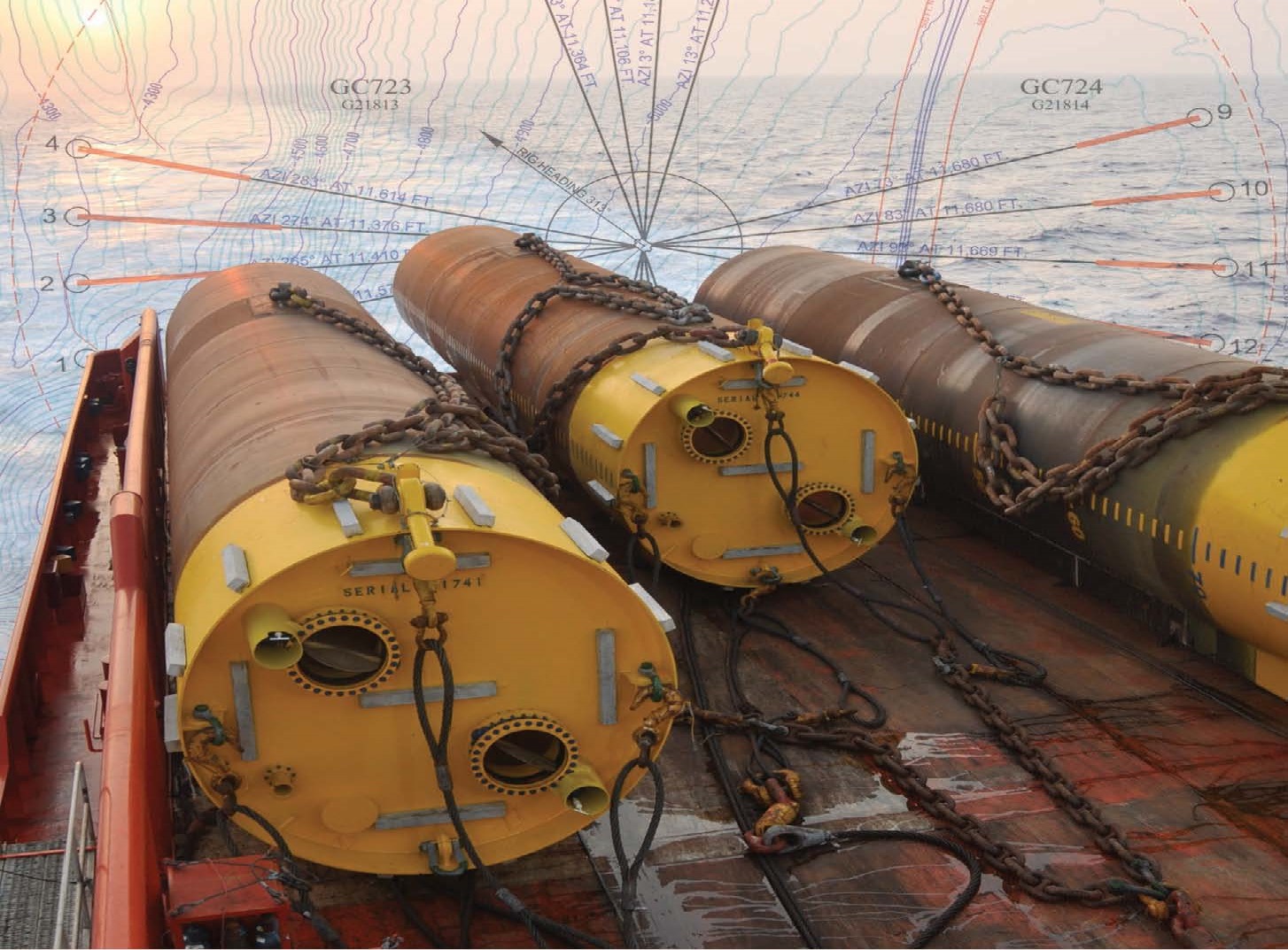
این انیمیشن نحوه اجرای لنگر مکشی را نشان می دهد این لنگرها مانند فونداسیون در سازه های دریایی عمل می کند محاسبات آنها خیلی خیلی مهم است چون تمام تاسیسات به آنها بستگی دارد
This animation shows how the suction anchor the anchor serves as the foundation offshore their calculation is very important because all plants depend on them
لنگرمکش، شمع مکش و سطل مکش

نصب لنگر مکش برای سازه های دریایی


یکی از سازه های کاربردی فراساحل لنگر مکش می باشد این سازه با عناوین مختلفی در مکان و شرایط خاصی نامگذاری می شود عملکرد تمام عناوین یکسال می باشد با توجه به آزمایشهای ژئوتکنیک دریایی از قبیل اشباع خاک ، جنس خاک ،CPT و کاربرد آن طول و قطر سازه فوق محاسبه می شود. هر چه قطر کمتر باشد طول زیادتر می شود و هرچه قطر بزرگتر باشد طول کمتر می شود. زمانی که تجهیزاتی روی آن سوار شود به عنوان شمع مکش می باشد و زمانی که سکوی نیمه شناور و سکوی پایه کششی به آن متصل باشد لنگر مکش یاد می شود و در صورتی همین سازه به عنوان پایه (فونداسیون ) توربین بادی وجکت ها در فراساحل استفاده می شود به عنوان سطل مکش یاد می شود. برای اولین بار کاربرد این سازه در دریا شمال برای سکوهای ثقلی مورد استفاده قرار گرفت

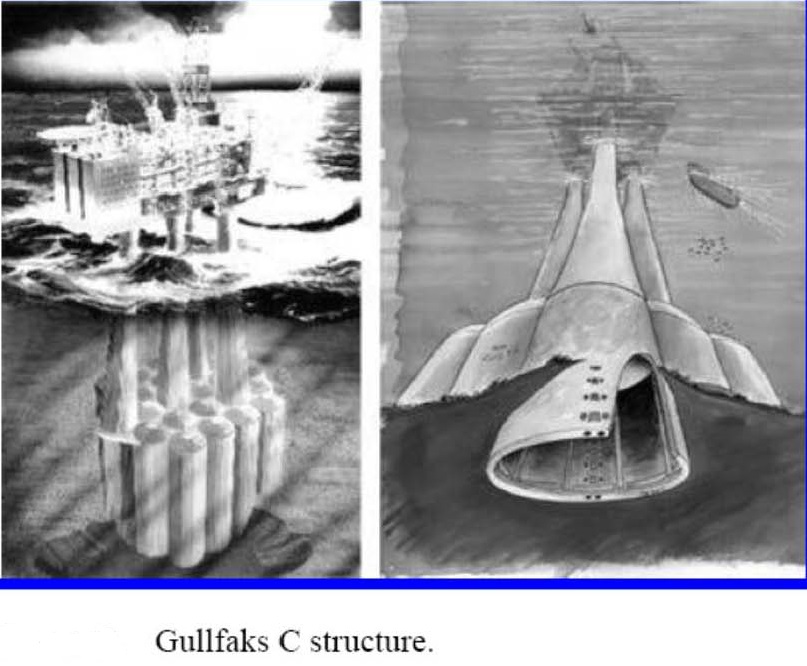
و بعدش در خلیج مکزیک درمورد استفاده قرار گرفته شد. با توجه به توسعه میدان های نفتی در دریاهای عمیق نیاز به لنگر مکش رو به افزایش است.
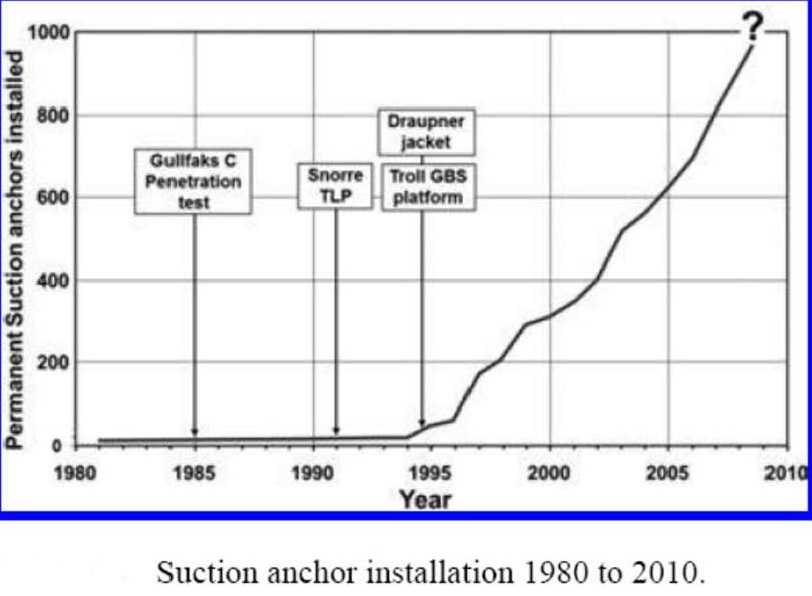
و درحال حاضر موسسه ژئوتکنیک نروژی (NGI) و ایالات متحده آمریکا روی این سازه تحقیقات گشترده ای انجام داده اند ثبت اختراع مختلف در ایالات متحده آمریکا گویای چنین پیشرفت روی این سازه بوده است می توانند به ثبت اختراع شماره 7059263 اشاره کرد
(U.S Patent #7059263) بنام OMNI-Max که در همین وبلاگ دنیای سازه های دریایی به آن ارشاره شده است


و همچنین لنگر عمق نفوذ (Deep Penetrating Anchor) (DPA) انقلاب بزرگی در طراحی و زمان بندی اجرای این سازه به راه افتاده است

تاریخچه / History
The development of Deep Penetrating Anchor started in 1996. Since then,national
and international patents have been awarded and extensive theoretical
analyses and model
scale tests (1:25) performed, leading up to the first and second 1:3
prototype tests and finally to the full-scale test in 2009
Statoil Hydro has been a partner since 1998 and contributed with both funding through the LOOP program as well as giving technical advice

The Norwegian Research Council has also supported the Gjøa tests through the DEMO2000 program. Two full-scale anchors were successfully installed in August 2009 and the Deep Penetrating Anchor is expected to be qualified by class society in the last quarter of 2009
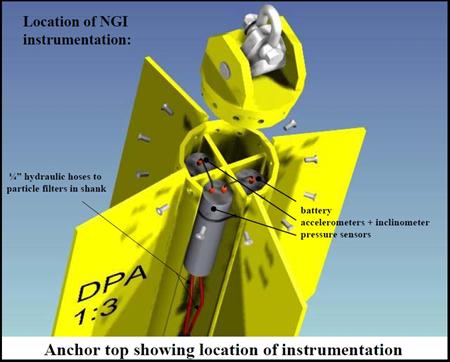
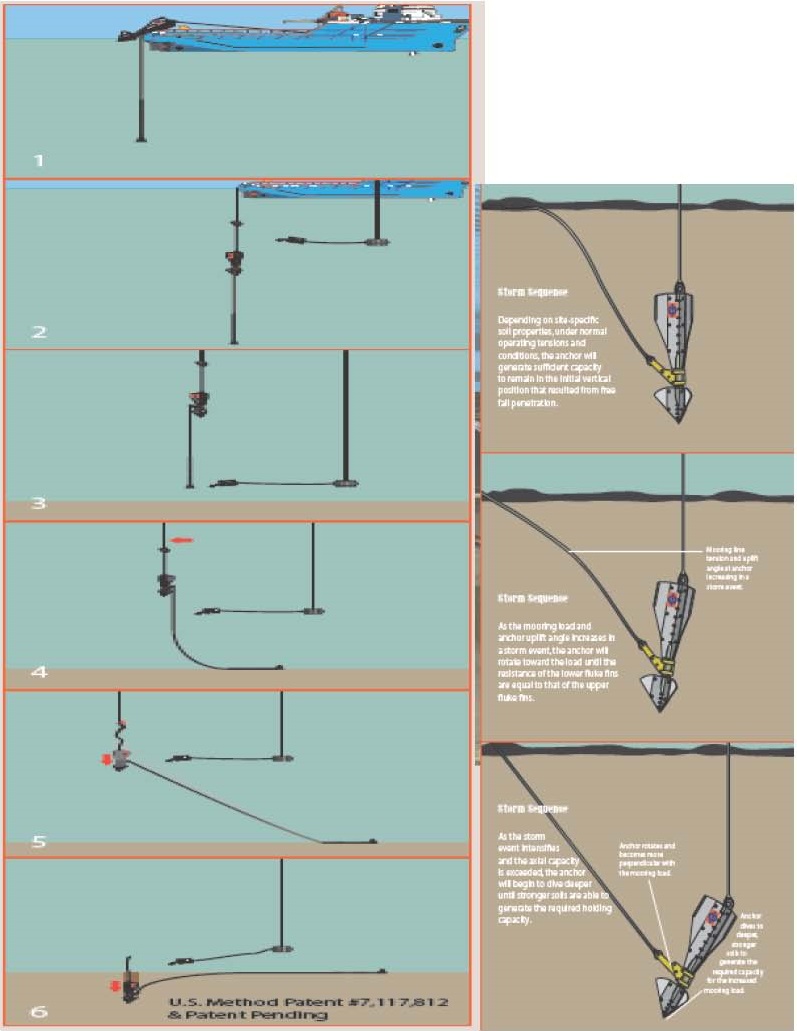
شرایط نصب لنگر مکش به شرایط اقلیمی دریا و اقیانوس دارد زمان در این کار بسیار مهم است این لنگرهای برای سکوهای نیمه شناور و سکوهای پایه کشی طراحی شده است
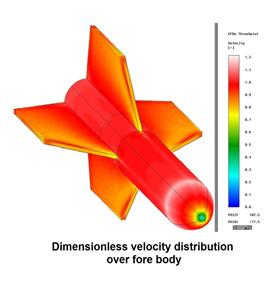
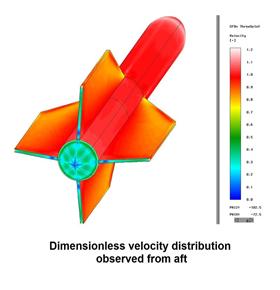
This video Deep penetrating Anchor simulation of chain behavior during anchor freefall
این فیلم شبیه سازی لنگر عمق نفوذ را نشان می دهد دقت کار و سرعت با توضحیات کامل


این لنگر عمق نفوذ مورد آزمایش های گوناگونی قرار گرفته است
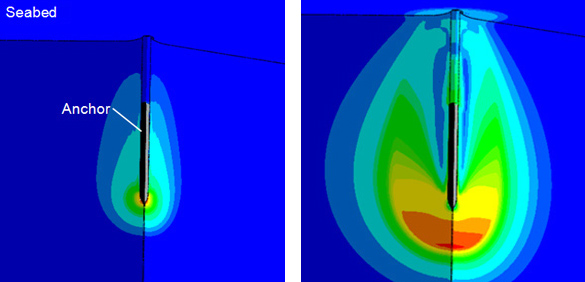

Anchor
لنگر ابزاری است که برای اتصال کشتی ، قایق و سکوهای نیمه شناور به نقطهای از کف دریا بکار میرود تا از حرکت شناور مذکور جلوگیری کند.لنگرها اصولاً بر دو گونه موقتی و دائمی هستند. لنگرهای موقتی را میتوان به بالا کشید و همراه با شناور برد ولی لنگرهای دائم را نمیتوان به بالا کشید بلکه برای جابجایی آن نیاز به اقدام تیم متخصص این کار است.تمامی وسایل مربوط به لنگر از قبیل زنجیر و دوّار لنگر و چشمی لنگر و دالان زنجیر و جرثقیل لنگر را لنگرافزار میگویند. کاربرد لنگرها بر اساس نوع، عملکرد، ظرفیت نگهداری، و طراحی، به طور معمول در عملیات مختلف مورد استفاده قرار می گیرند.
اجزاء لنگر
میله
ناخن
گلویی
تاج
لبه تاج
زمینگیر
وزنه
زنجیر مهار
کلاف
حلقه گردان
انواع لنگر
لنگر انگلیسی با دو شاخه زمینگیر
لنگر شخمی
لنگر قارچی
لنگر شخمی
لنگر دستهدار
لنگر بیدسته
لنگر تنگ هم
لنگر انگلیسی
لنگر چنگکی
لنگر کجبیلی نوعی لنگر به شکل کجبیل که مناسب بسترهای ماسهای سخت یا دارای پوششهای گیاهی است.
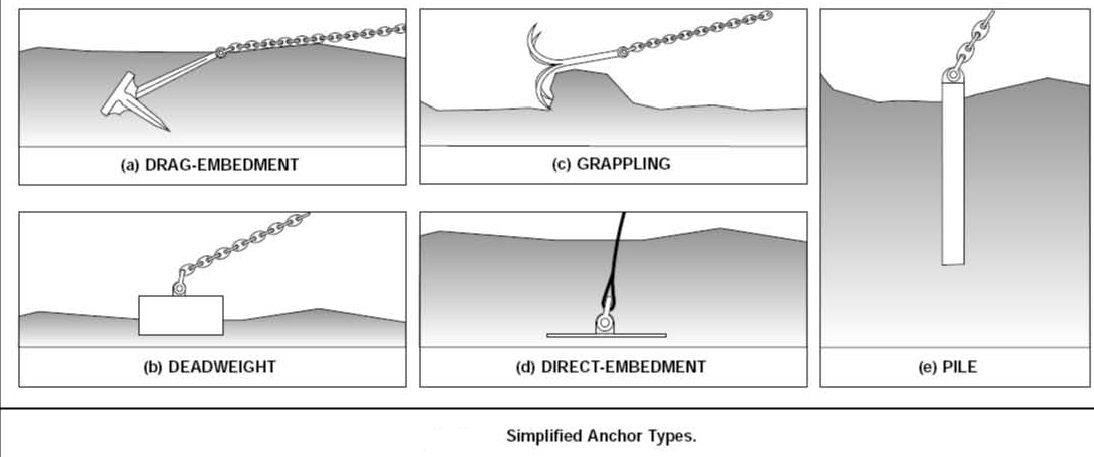
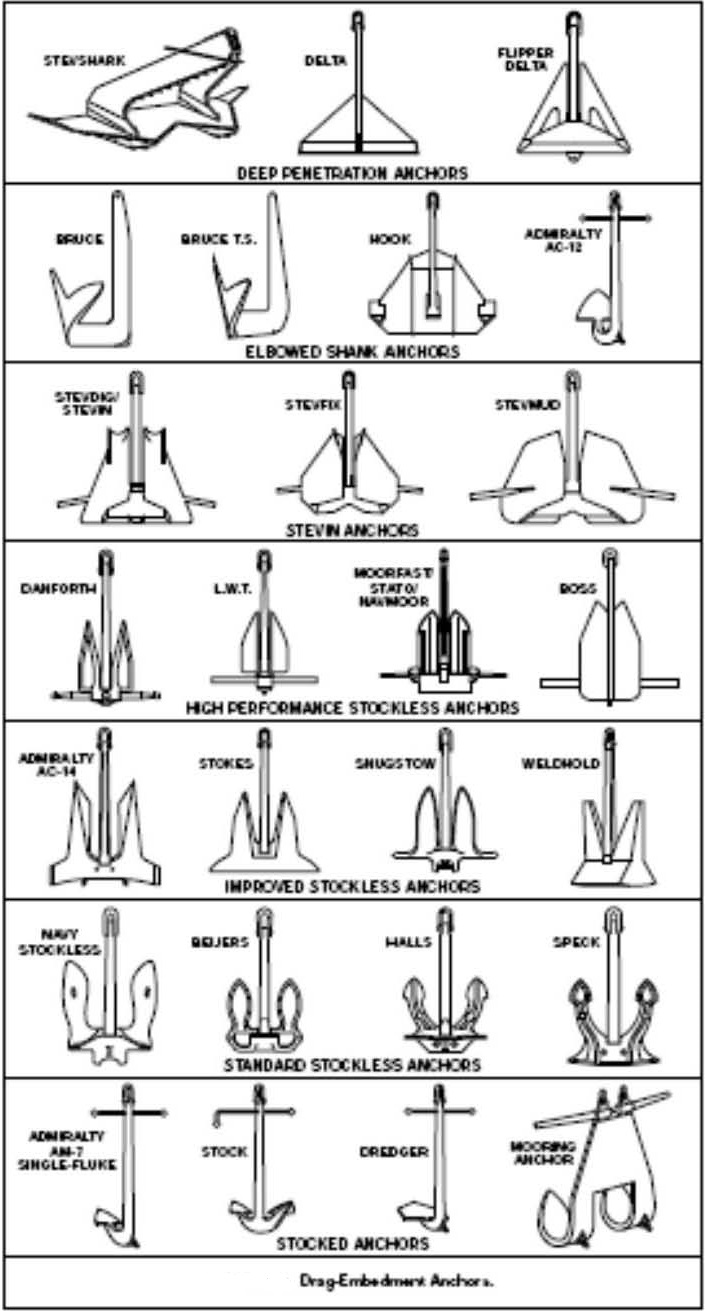
Anchors can be roughly divided into five types
· Drag-embedment anchors,
· Deadweight anchors or clumps,
· Grappling devices,
· Direct-embedment anchors, and
· Pile anchors.


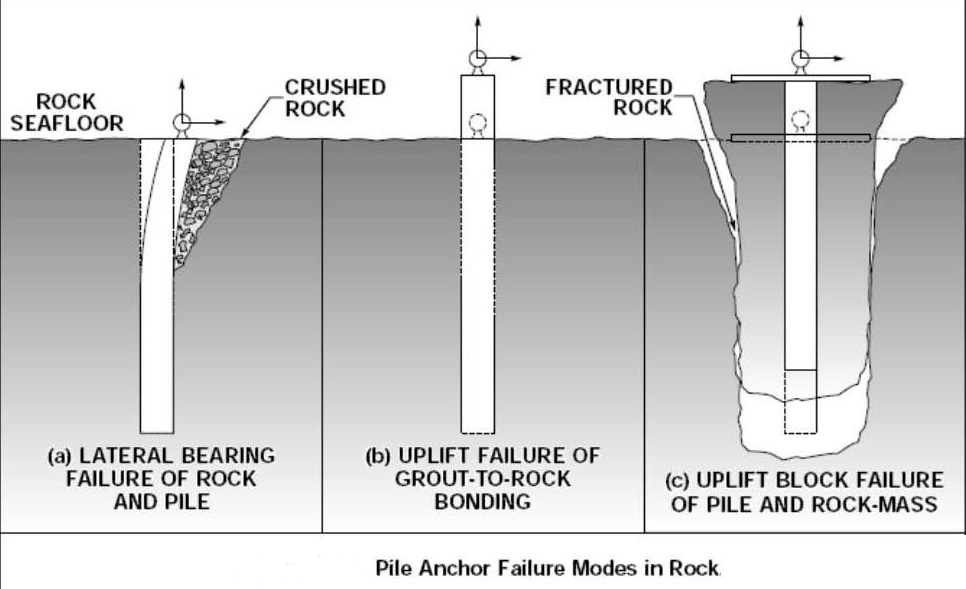
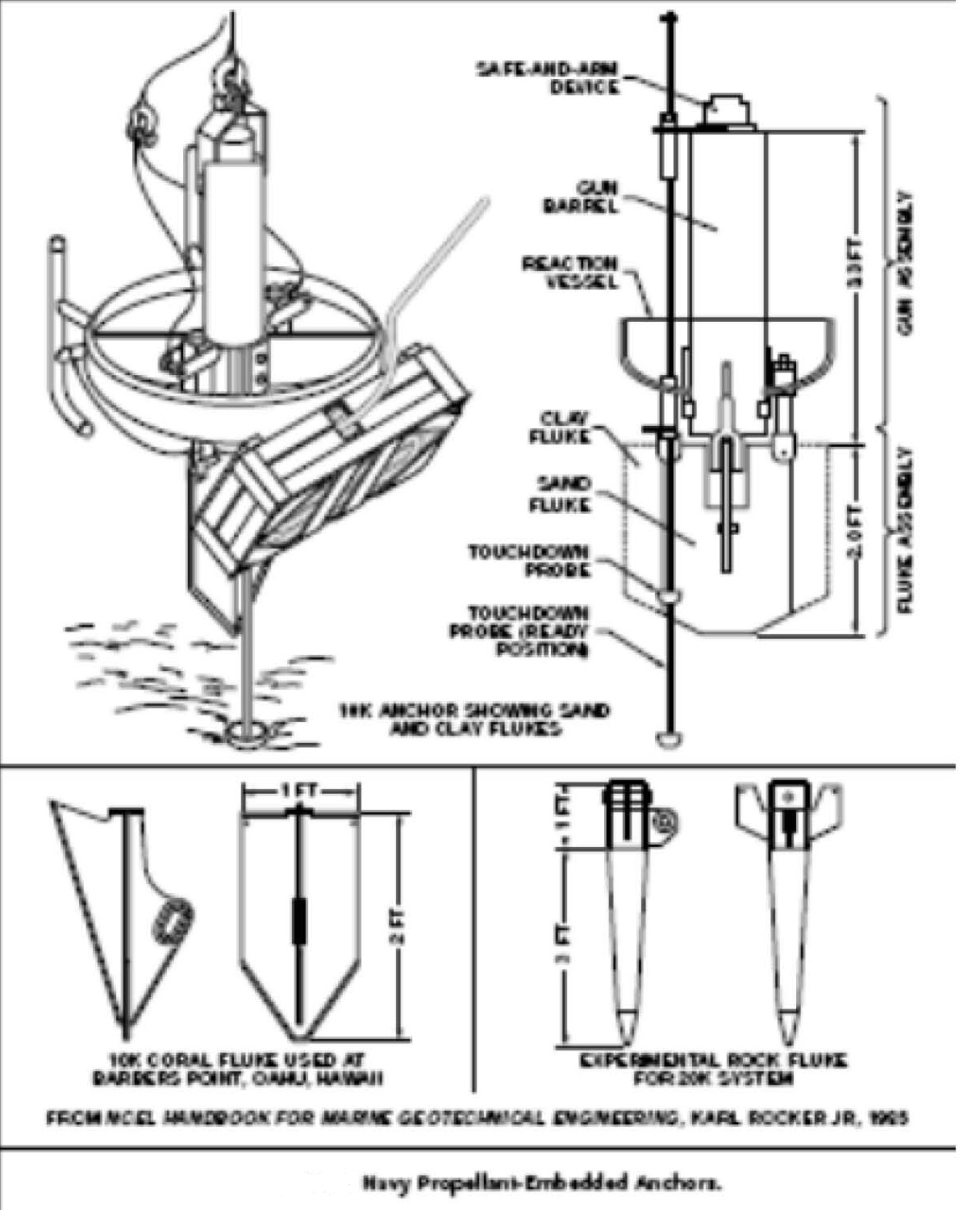
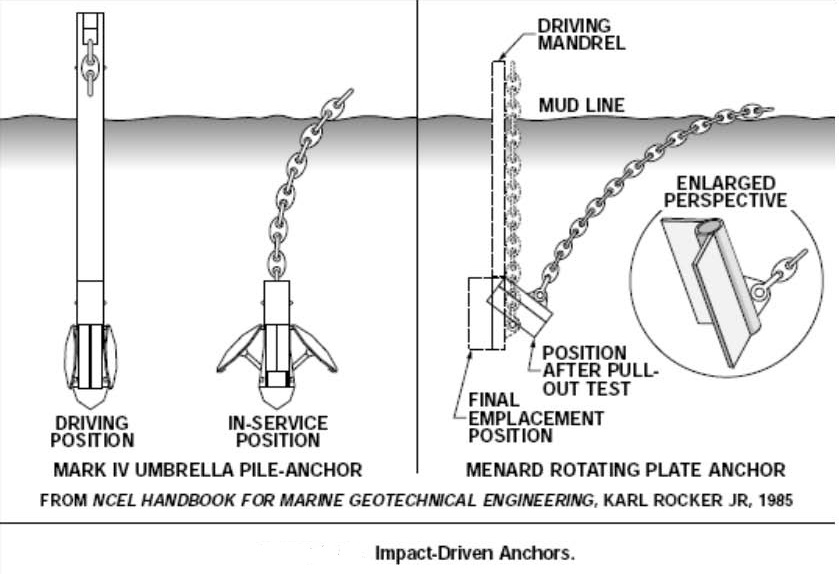
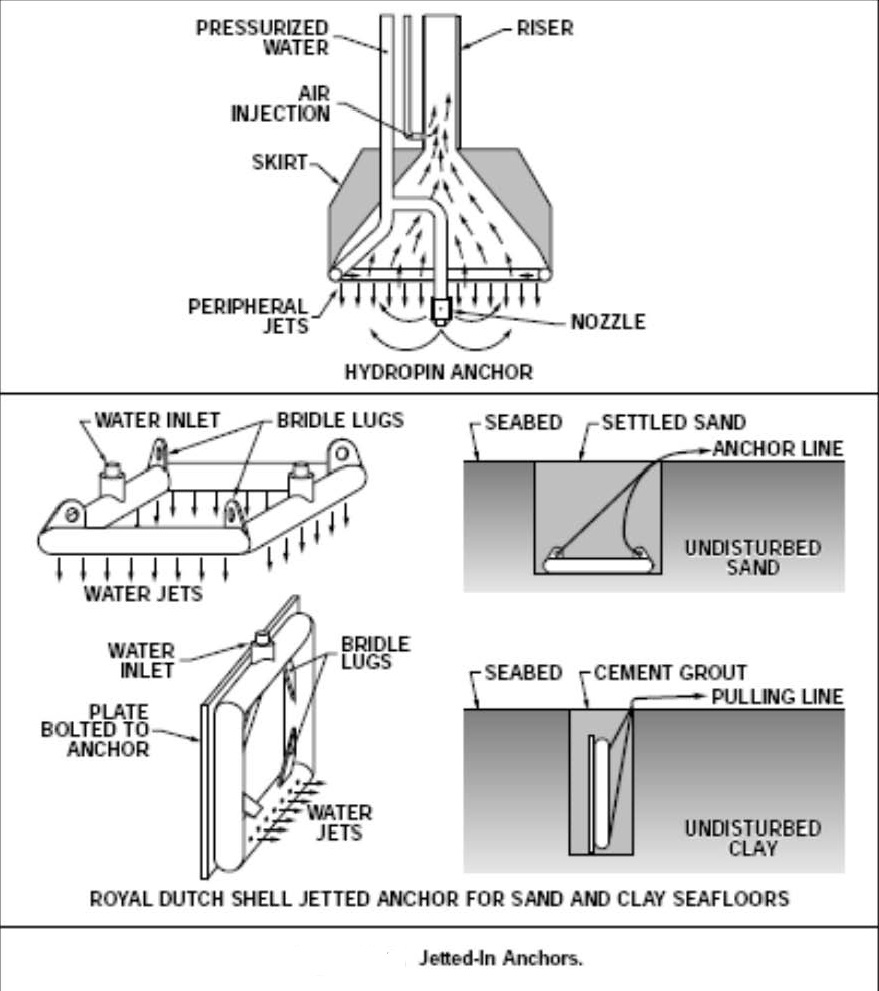
PILE FOUNDATIONS AND ANCHORS
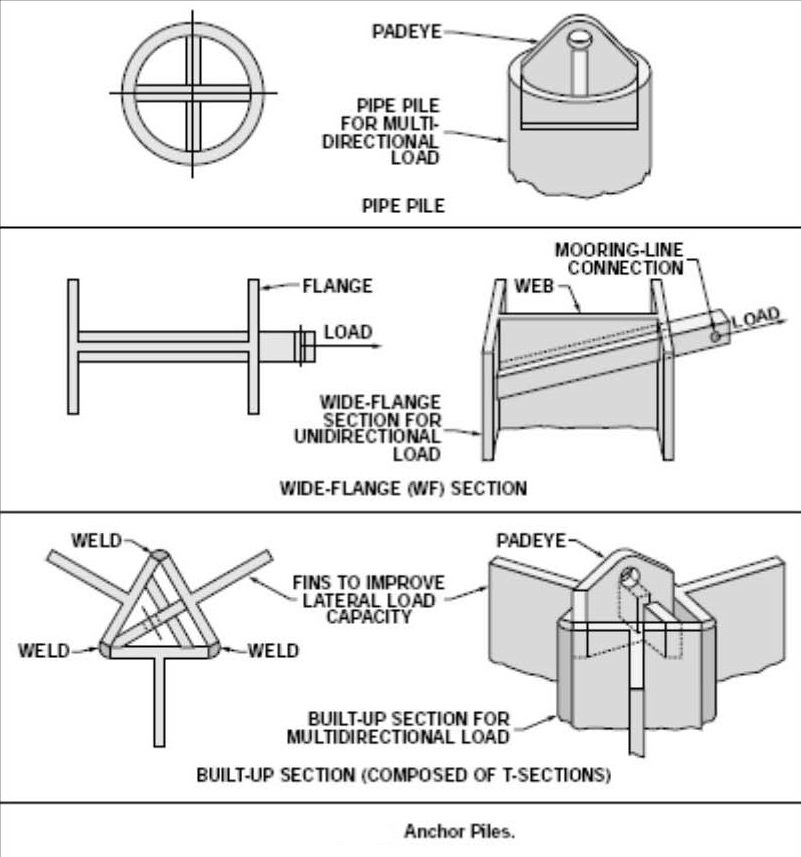
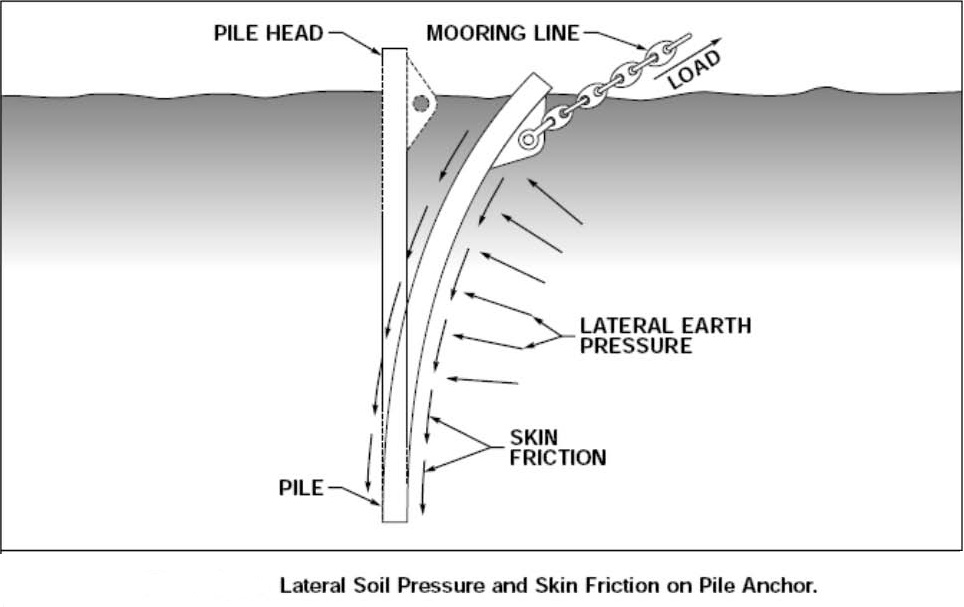

اولین فرمول و رابطه محاسبه لنگر مکشی ،با جمع آوری رابط می توانید در نرم افزار اکسل فرم آن را بنویسید

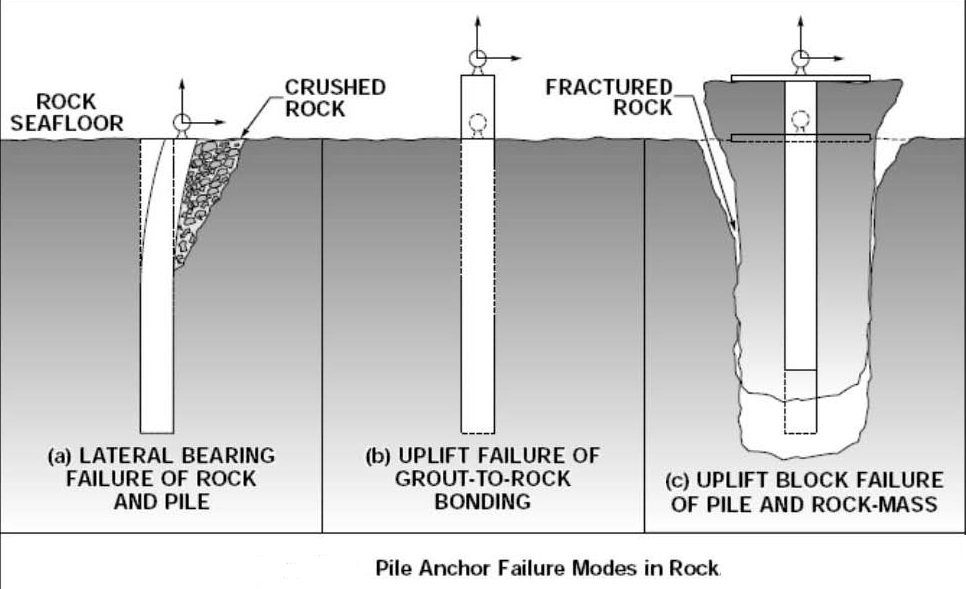
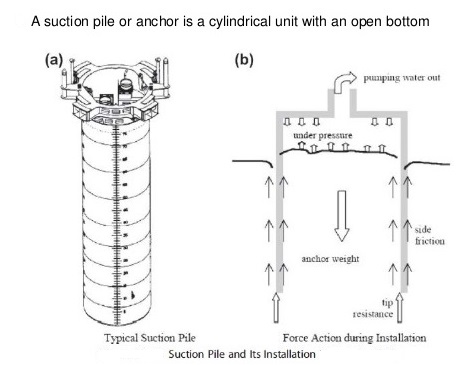
Suction
Suction caissons (also referred to as suction anchors, suction piles or suction buckets) are a new form of offshore foundation that have a number of advantages over conventional offshore foundations, mainly being quicker to install than piles and being easier to remove during decommissioning. Suction caissons are now used extensively worldwide for anchoring large offshore installations to the seafloor at great depths. Oil and gas recovery at great depth could have been a very difficult task without the suction anchor technology, which was developed and used for the first ti.me in the North Sea 30 years ago
The use of suction caissons/anchors has now become common practice worldwide. Statistics from 2002 revealed that 485 suction caissons had been installed in more than 50 different localities around the world, in depths to about 2000 m. Suction caissons have been installed in most of the deep water oil producing areas around the world: The North Sea, Gulf of Mexico, offshore West Africa, offshore Brazil, West of Shetland, South China Sea, Adriatic Sea and Timor Sea. No reliable statistics has been produced after 2002, but the use of suction caissons is still rising
محفظه مکش (همچنین به عنوان لنگر مکش، شمع مکش یا سطل مکش نامیده می شود) یک شکل جدید از فونداسیون های فراساحلی است که این ساز ه دارای یک تعدادی مزیت های برای فوانداسیون فراساحلی برخودار می باشد، به طور عمده به دلیل اینکه سرعت اجرای نصب آن نسبت به شمع آسان تر بودن و در مدت زمان صرفه جوی می شود. محفظه مکش در حال حاضر در سراسر جهان برای مهار تاسیسات بزرگ فراساحلی به بستر دریا در اعماق زیاد استفاده می شود. نفت و گاز در عمق بزرگ دریا یک کار بسیار دشوار می باشد بدون فن آوری لنگر مکش امکان ندارد، برای اولین بار از این فن آوری در استخراج نفت و گاز از دریا شمال در دهه 80 میلادی مورد استفاده قرار گرفت است.
استفاده از محفظه های مکش / لنگر (مهار) در حال حاضر روش معمولی در سراسر جهان است. آمار از سال 2002 نشان داد که 485 محفظه مکش در بیش از 50 محل مختلف در دنیا ، در اعماق به حدود 2000 متر نصب شده است. محفظه مکش در بسیاری از مناطق تولید نفت در آب های عمیق در سراسر جهان نصب شده است: دریای شمال، خلیج مکزیک، اقیانوس اطلس جنوبی آفریقا ( خلیج گینه ) و برزیل، اقیانوس اطلس شمالی غرب از جزایر شتلاند، دریای چین جنوبی، دریای آدریاتیک و دریای تیمور. هیچ آمار معتبر پس از سال 2002 وجود ندارد. اما استفاده از محفظه مکش هنوز در حال افزایش است.
Description
A suction caisson can effectively be described as an upturned bucket that is embedded in the marine sediment. This embedment is either achieved through pushing or by creating a negative pressure inside the caisson skirt: both of these techniques have the effect of securing the caisson into the sea bed. The foundation can also be rapidly removed by reversing the installation process, applying an overpressure inside the caisson skirt
The concept of suction technology was developed for projects where gravity loading is not sufficient for pressing foundation skirts into the ground. The technology was also developed for anchors subject to large tension forces due to waves and stormy weather. The suction caisson technology functions very well in a seabed with soft clays or other low strength sediments. The suction caissons are in many cases easier to install than piles, which must be driven (hammered) into the ground
Mooring lines are usually attached to the side of the suction caisson at the optimal load attachment point, which must be calculated for each caisson. Once installed, the caisson acts much like a short rigid pile and is capable of resisting both lateral and axial loads. Limit equilibrium methods or 3D finite element analyses are used to calculate the holding capacity
یک محفظه مکش به طور موثر می تواند مانند یک سطل وارونه باشد که داخل آن رسوبات دریایی تعبیه شده است. به دو روش می توان محفظه را در محل خودش قرار داد از طریق هل دادن که این کار توسط نیرو وزنی خود محفظه انجام می شود، یا با ایجاد فشار منفی در داخل محفظه و بستر دریا: هر دو این روش ها دارای تامین امنیت برای پایداری سازه به بستر دریا است.
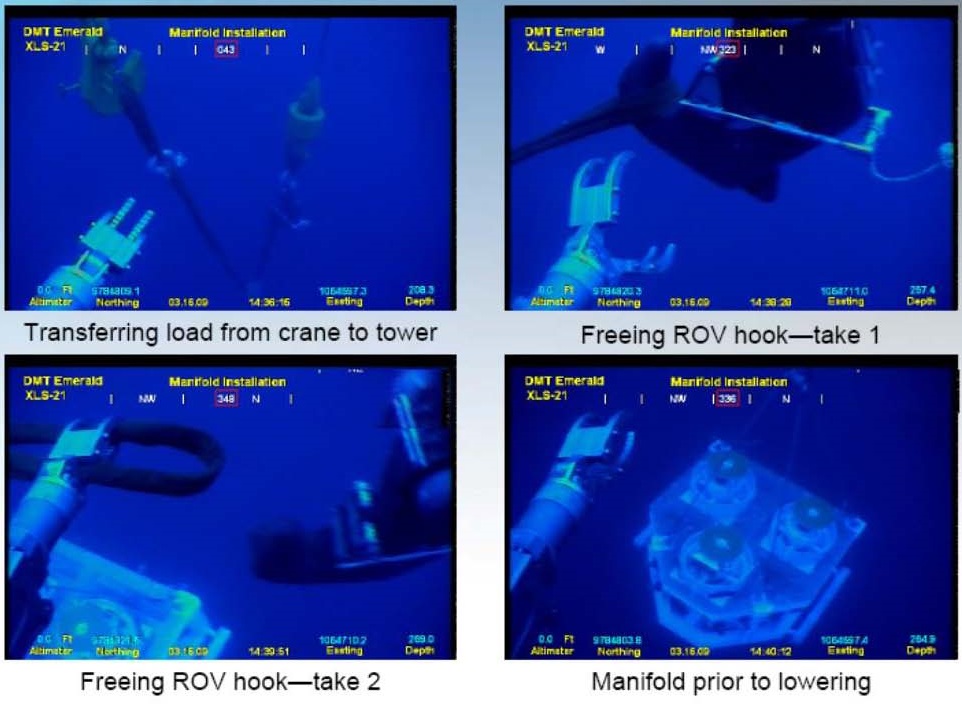
در مورد این انیمیشن نصب شمع مکشی (لنگر مکش) اولین کاری که باید صورت بگیرد طبق اطلاعات نقشه برداری محل آن مشخص شده است هیدروگرافی و توپوگرافی منطقه نقش اساسی را بازی می کنند این کار توسط کشتی های مخصوص انجام می شود چون پایه طراحی (flowline) درصدی به این کار ربط دارد محل ها استقرار لنگر مکش توسط دستگاه GPS و با کمک چشم دریا (ROV) و بواسطه بادکنک های کوچک مشخص می شود
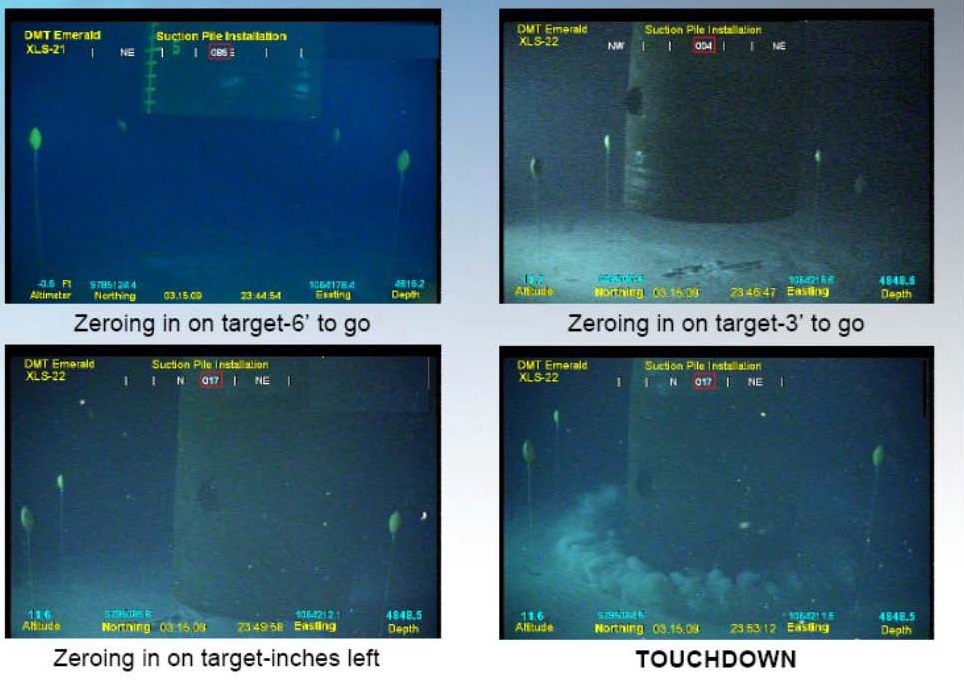

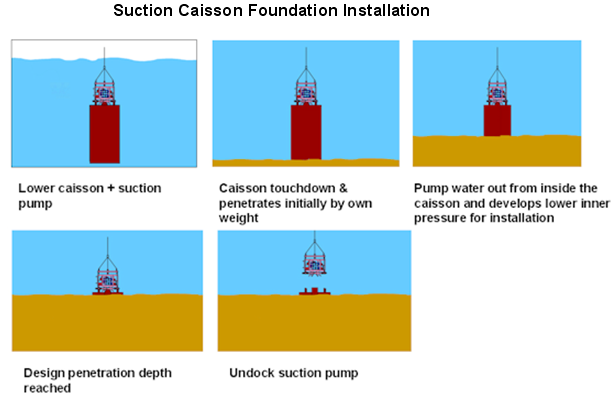

همانطور که در انیمیشن مشخص است لنگر مکش در محل خود مستقر می شود این مانند اینکه شما از ساختمان 20 طبقه یک میخ را در محل مورد نظر قرار بدهید.

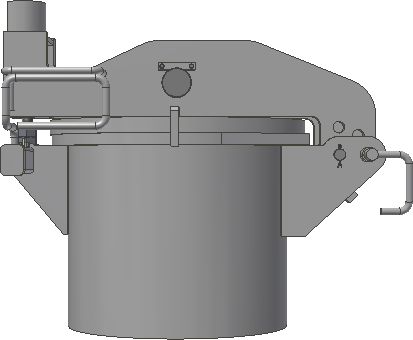
همانطور که می دانید کار طراحی یک خط صاف و تمیز دقیق است ولی کار اجرا با واقعیت ها درگیر است وان چیزی که روی کاغذ کشید می شود نیست تا حدودی نزدیک آن است حال لنگر مکش توسط وزن خود به پایین کشیده می شود بیشترین وزن لنگر مکش در دنیا 200 تن است. حال کابل های متصل توسط چشم دریا جدا می شود .حال نوبت بسته شدن دریچه های پشت لنگر مکش است این دریچه معروف هستند بنام(Suction Pile Vent Hatch) این دریچه ها به دو نوع طراحی شده اند.
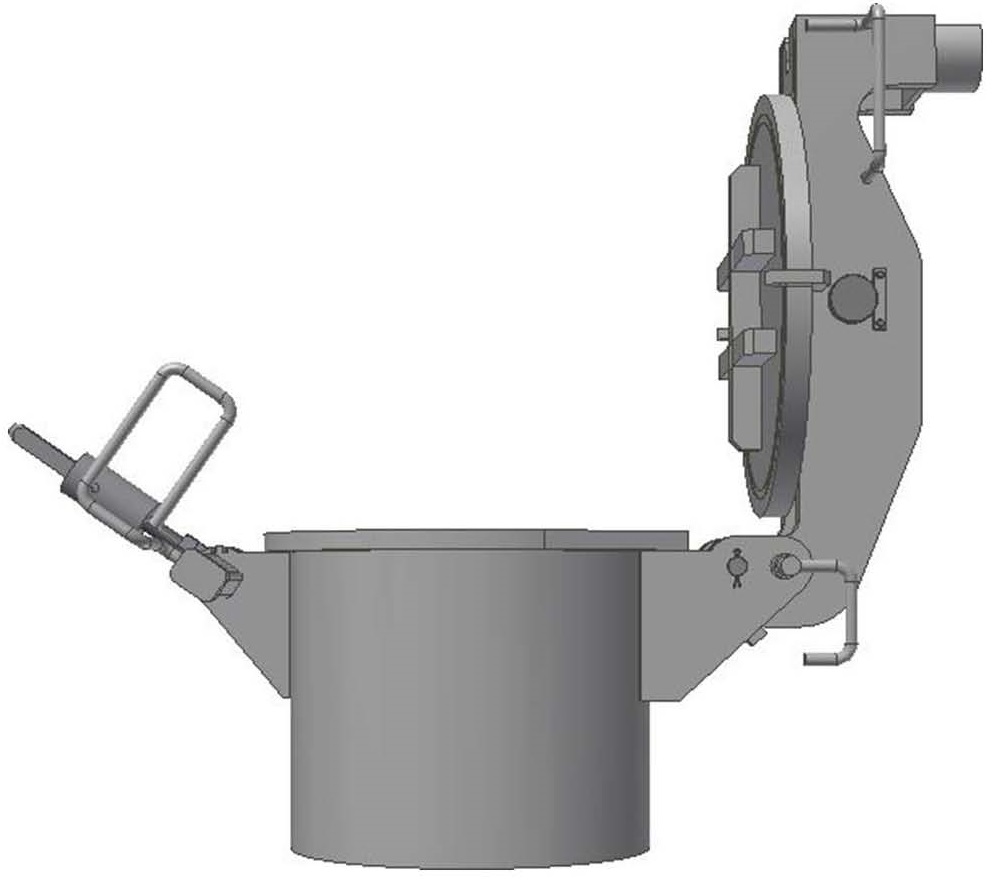
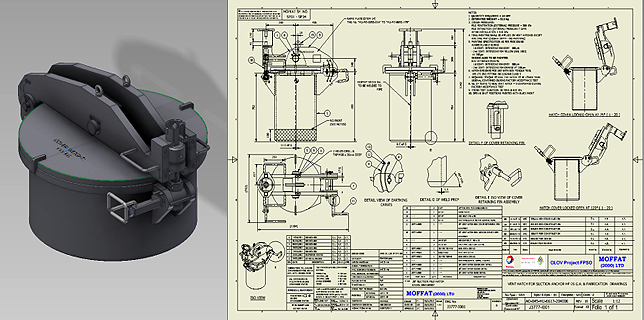
اولی بنام Hinged Design اقتصادیتر است

دومی بنام Butterfly Valve Design اطمینان تر است , ضریب ایمنی بالا دارد

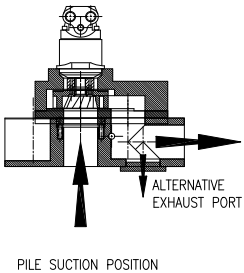
حال نوبت برداشتن Dummy Hot Stab است

تا عمل مکش صورت بگیرد حال نوبت ابزار(stabs and Receptacles) (نرو ماده) است
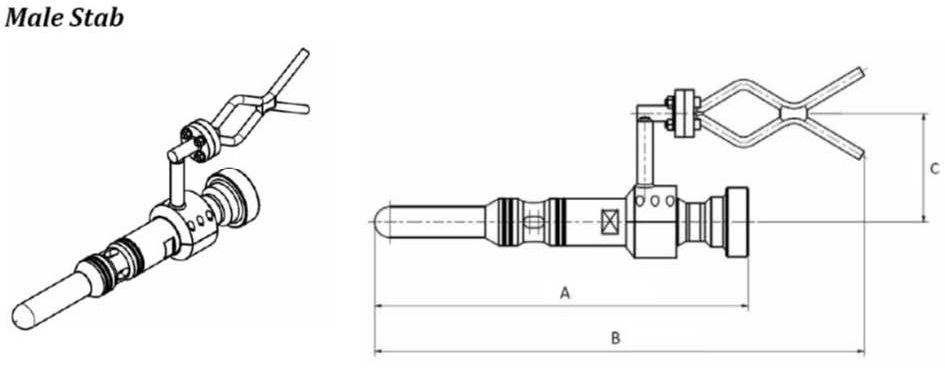

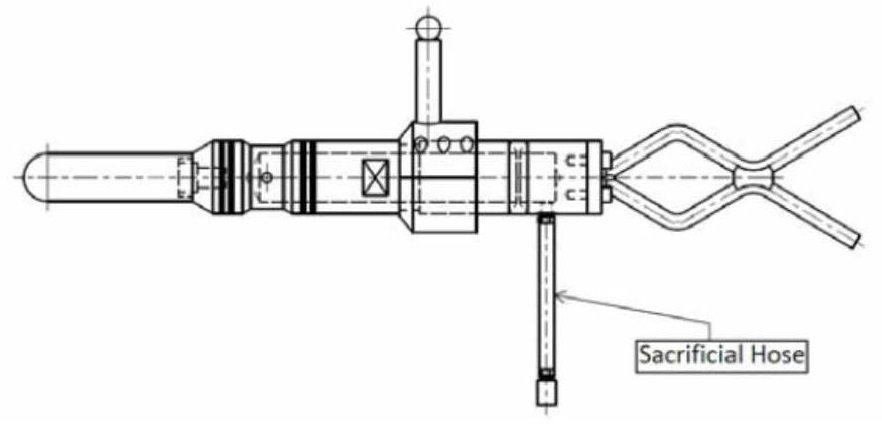

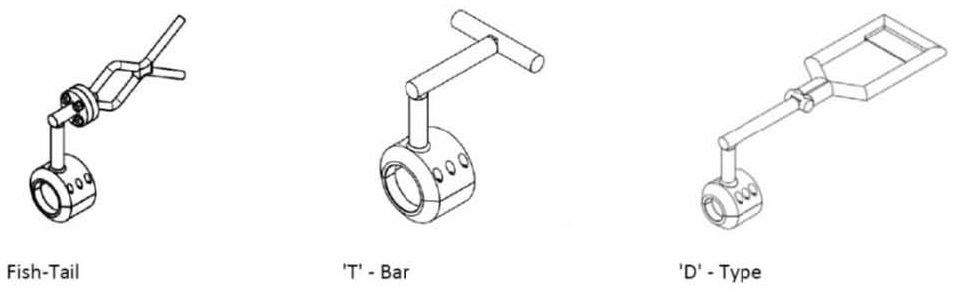
انواع دستگیره ها عبارتند
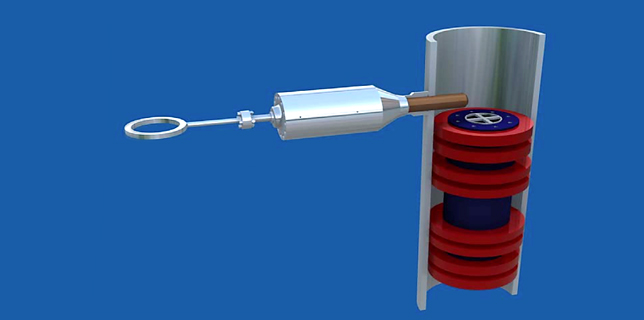
با جا گذاشتن این ابزار در معفذه عمل مکش صورت می گیرد لنگر یا شمع مکش به سمت پایین هدایت می شود با این کار محکم به بستر دریا متصل می شود
حال باید لنگر مکش را تراز کنم این عمل توسط دستگاه چشم دریا و عمل مکش انجام می شود مانند دوربین نقشه برداری پیچهای طراحی شده تا روی سازه تراز شود در هر صورت باید سطح تراز داشته باشم در مورد ترازهای زیر دریا چیزی که نظر من را جلب کرد حداکثر 20 روز بعد این ترازها نابود می شوند.به خاطر موقعیت آن در زیردریا و کاربردی هم ندارد.
حال نوبت عملیات pig launchers and Receiver

Riser Alignment Tool (RAT) is flexible and versatile solution for checking inclination of a riser or similar subsea structures. The RAT can be installed on deck on a riser between a diameter of 150mm (6”) to 350mm (14”) with proper inserts and can be removed easily and quickly subsea by an ROV.
The RAT is electrically isolated so it won`t lead to any corrosion of the host structure.
Features:
Easily removed by ROV
Easily read from ROV
Corrosion resistant material
Proven rugged design
Specifications:
Dimensions (Winch) 540 x660 x200mm
Weight in Air 26kg
Weight in Seawater 11.5kg
Accuracy ±0.25º
Max. Subsea Deployment 20 days
Max. Working Depth 6000msw*
Range ±3º
*Depending on the Bullseye used
Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics III,Vaughan Meyer,CRC Press,2015
این کتاب درباره سرحدهای ژئوتکنیک فراساحلی می باشد، که دارای 1398 صفحه و در 2 جلد می باشد. مجموعه ای از مقالات ارسالی به موسسه ژئوتکنیک نروژ می باشد که توسط Vaughan Meyer جمع آوری شده است. با این عناوین
Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics III,Vaughan Meyer,CRC Press,2015
The titles
This file is password
Password: CE-MS MS.c Bijan Mohammadi
All text and change the color to use to download it
دانلود/Download کلمه عبور/ Password

Volume 1
*Keynotes
The suction foundation technology
Geotechnics for wells top-hole section and conductor
The effects of pile ageing on the shaft capacity of offshore piles in sand
A FE procedure for calculation of cyclic behaviour of offshore foundations under partly drained conditions
Geohazard risk evaluation and related data acquisition and sampling program for the methane hydrate offshore production test
Deterministic and probabilistic advances in the analysis of spudcan behavior
*Suction anchors and caissons
Installation of suction caissons for an asymmetrical support structure in sandy soil
Simplified earthquake analysis for wind turbines and subsea structures on closed caisson foundations
Laterally loaded suction caissons with aspect ratio of one
Seismic response of bucket foundations for offshore wind tower using dynamic centrifuge tests
Friction degradation and strength regain along suction piles in soft deep water Gulf of Guinea clays
Suction pile foundation for a PLET subsea structure
Suction caisson extraction resistance in Gulf of Guinea clay
Performance of a shallow skirted foundation for TLP mooring in carbonate silt
Calculation of undrained holding capacity of suction anchors in clays
Interpretation of centrifuge tests of suction anchors in reconstituted soft clay
CAISSON_VHM: a program for caisson capacity under VHM load in undrained soils
Suction anchor geotechnical design practice: A case study
Centrifuge model test for bearing capacity evaluation of hybrid suction foundation on clay under vertical and horizontal loads
Pullout resistance of horizontal and inclined loaded suction anchor installed in silty sand via centrifuge modelling
Skirt penetration resistance in carbonate soils from the CPT
Horizontal capacity of multiple suction anchors using numerical analysis
Dynamic behaviour of mono bucket foundations subjected to combined transient loading
Novel monitoring solutions solving geotechnical problems and offshore installation challenges
Effect of torsion on suction piles for subsea and mooring applications
Comparison of design methods for axially loaded buckets in sand
Caisson capacity in undrained soil: Failure envelopes with internal scooping
P–y curves for bucket foundations in sand using finite element modeling
*Pipelines, risers and subsea earthworks
Seabed stiffness model for steel catenary risers
Ultimate uplift capacity of buried pipelines in undrained clay
Evaluation of a toroid for model pipeline testing of very soft offshore box core samples
Excess pore pressure redistribution beneath pipelines: FEA investigation and effects on axial pipe-soil interaction
Pipeline embedment and consolidation beneath on-bottom pipe model in kaolin clay
The soil strength degradation influence in the axial pipe-soil resistance
Pipe-Soil Interaction: Recent and future improvements in practice
Predicted and observed settlements of a subsea rock installation – comparison between field measurements and FE simulations of soft North Sea clay
Effects of different loading time histories on fatigue design of steel catenary risers using nonlinear riser-soil interaction models
A new torsional shear device for pipeline interface shear testing
Large scale experiments on the riser-soil interaction in clay
An integrated approach to pipeline burial in the 21st century – The current state-of-the-art
Direct shear interface tests for pipe-soil interaction assessment
Evaluation of pipe-soil interaction in liquefied soil
Pipe-soil interaction under rapid axial loading
Mechanical trencher modelling in hard ground: State-of-the-art
Finite element analysis of soil damping for pipeline slugging
Geotechnical considerations for pipeline stabilization design using rock berms
Pipe-soil interaction mechanism during pipeline upheaval buckling in loose saturated sand
Study of vertical pipe-soil interaction based on Coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian method
Stress level effects on plane-strain pipe uplift resistance
Theoretical analysis and model test for pipeline protection from dragged anchors
A discrete element study on upheaval ratcheting behavior of pipelines buried in sand
An investigation on existing nonlinear seabed models for riser-fluid-soil interaction studies in steel catenary risers
Geotechnical design and construction aspects of a pipeline-escarpment crossing
*Piled foundations
Modelling of laterally loaded screw piles with large helical plates in sand
Design methodology for cyclically and axially loaded piles in chalk for Wikinger OWF
Full scale offshore verification of axial pile design in chalk
Centrifuge investigation of the axial cyclic behaviour of a single pile used for the foundation of a jacket type offshore wind turbine
Review of pile driving results for the Maui and Maari developments in the Taranaki basin of New Zealand
Cyclic pile load tests combined with laboratory results to design offshore wind turbine
Foundations in chalk
Comparison of pile bearing capacity from CPT and dynamic load tests in clay considering soil setup
The use of pipe piles for creating ice protection barrier
Improvement of bearing capacity of vibratory driven open-ended tubular piles
Small strain overlay to the API p-y curves for sand
Boulder-soil-pile dynamic interaction
Driven pile design in weak rock
Effect of soil set-up during interruption of offshore pile driving
Axial capacity design practice for North European wind-turbine projects
Lessons learned from pile driving and monitoring in gravels on the Northstar Artificial Island
Innovative design of foundations – offshore wind farm substation
A preliminary experimental study on the mechanism of local scour at pile groups in steady currents
Interpretation difficulties of pile set-up in sand
Evolution of driving resistance during driven pile installation
CPT-based pile shaft friction in calcareous sands of western Indian offshore
Synthesis of pile driving data in South East Asia
Case studies – predicting soil resistance to driving in South East Asia
Axial capacity ageing trends of piles driven in silica sands
In situ and laboratory tests in dense sand investigating the helix-to-shaft ratio of helical piles as a novel offshore foundation system
Re-assessment of pile driveability predictions on sites offshore Nigeria
Numerical implementation of soil-pile interaction models for monotonic and reversed axial loading
Ultimate lateral resistance of laterally loaded piles in undrained clay
Deepwater jetted piles: Numerical modeling of jetting action and axial bearing capacity
Centrifuge model tests on laterally monotonic and cyclic pile-soil interaction of a tetrapod jacket foundatio
*Monopiles
Model pile response to multi-amplitude cyclic lateral loading in cohesionless soils
On the development of a hybrid foundation for offshore wind turbines
Alternative p-y curve formulations for offshore wind turbines in clays
Improving the lateral resistance of offshore pile foundations for deep water application
New design methods for large diameter piles under lateral loading for offshore wind applications
Cyclic lateral loading of monopiles for offshore wind turbines
Observed variations of monopile foundation stiffness
Design of large diameter monopiles in chalk at Westermost Rough offshore wind farm
Influence of vertical loads on the behavior of laterally loaded large diameter pile in sand
Predicting monopile behaviour for the Gode Wind offshore wind farm
Evaluation of a new p-y approach for piles in sand with arbitrary dimensions
Experimental trends from lateral cyclic tests of piles in sand
Effect of relative pile’s stiffness on lateral pile response under loading of large eccentricity
Numerical modelling of large diameter piles under lateral loading for offshore wind applications
Volume 2
*Shallow foundations
Prediction and worked example for a sliding foundation on soft clay
Effects of drainage on the response of a sliding subsea foundation
Undrained bearing capacity of skirted mudmats on inclined seabeds
Three-dimensional limit analysis of rectangular mudmat foundations
Collision of double hull tanker with gravity base foundation of offshore wind turbine: case of horizontal drift and swell
Some key aspects in geotechnical design of GBS foundations on sand
A framework for the design of sliding mudmat foundations
Undrained vertical bearing capacity of perforated shallow foundations
Simulation of a full-scale test on a gravity base foundation for offshore wind turbines using a high cycle accumulation model
System integration of direct on-seabed sliding foundations
*Anchoring systems
Pullout capacity of plate anchors in sand for floating offshore wind turbines
Centrifuge model study on pullout behavior of plate anchors in clay with linearly increasing strength
Large deformation numerical analysis of plate anchor keying process
The role of partly remoulded clay in fluke and plate anchor design
Numerical modeling of drag anchors of floating structures – comparison of ultimate holding capacity with limit equilibrium methods
Design and performance of suction embedded plate anchors
Soil flow mechanism around deeply embedded plate anchors during monotonic and sustained uplifts
Comparison between FEM analyses and full-scale tests of fluke anchor behavior in silty sand
Dynamically Installed Anchors: Performance of embedded mooring chain profile in clay
A review of anchor technology for floating renewable energy devices and key design considerations
Numerical modelling of the SEPLA during keying process
Behavior of Suction Embedded Plate Anchors with flap during keying in clay
Chain configuration in sand, theory and large scale field testing
Cyclic response of shallow helical anchors in a medium dense sand
Numerical investigation on line tension-induced pore pressure accumulation around an embedded plate anchor
Behaviour of OMNI-Max anchors under chain loading

ایده طراحی لنگر OMNI-MAX بر گرفته از لنگرهای مکش دیگر از جمله لنگر مکش صفحه جا سازی شده می باشد دامنه درگیر این سازه نسبت به لنگر مکشی بیشتر است این لنگر فوق در ایالات متحده آمریکا به شماره ثبت اختراع 7059263 ثبت شده است. در مورد لنگرها در همین وبلاگ دنیای سازه های دریایی درباره آن نوشته شده است.
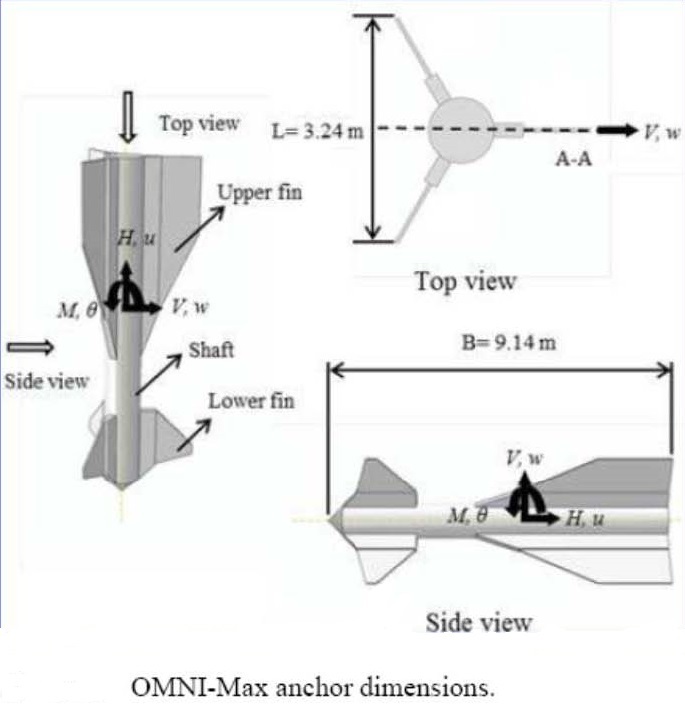

این مقاله درباره لنگر OMNI-MAX می باشد
All text and change the color to use to download it
کلمه عبور/Password دانلود/Download

*Geohazards and integrated studies
Predictions of ice scour loads from small scale tests under 1 g conditions
Areas 2 and 5 offshore Mozambique: Mass-movements on a deep-water margin with scant adjacent shelf
Turbidity current hazard assessment for field layout planning
Bayesian mechanistic imaging of two-dimensional heterogeneous elastic media from seismic geophysical observations
Optimization of deep-water pipeline routes in areas of geologic complexity – an example from the Southern Gulf of Mexico
Understanding the element of time in probabilistic submarine slope stability analyses
Effect of fines on mechanical properties of methane hydrate bearing sands
Numerical analysis of submarine debris flows based on critical state soil mechanics
The life cycle of geohazards within an offshore engineering development
Numerical analysis of stability of seafloor slope under linear waves
Offshore 1D infinite slope modeling in seismic conditions with OpenSees
Numerical simulations of shallow gas migration in vicinity of platforms in offshore Malaysia: Effects of relief wells on excess pore pressure dissipation
Geotechnology – Converting site investigations into 3D geotechnical models
Weak interlayers effects on seismic performance of a deepwater slope
Integration of very-high-resolution seismic and CPTU data from a coastal area affected by shallow landsliding – the Finneidfjord natural laboratory
Influence of gas hydrate dissociation on mechanical properties of gas hydrate-bearing sediment
*Soil characterisation and modelling
Effect of pore pressure build-up on the seismic response of sandy deposits
Potential of estimating relative density by measuring shear wave velocity in field and in laboratory
Strength of a carbonate silt at the solid-fluid transition and submarine landslide run-out
Results of geotechnical characterization in the laboratory of clays from offshore Mozambique
Temperature effects on laboratory measured strength on deep water soft clays
Procedures for estimating hysteretic foundation damping
Development of nonlinear foundation springs for dynamic analysis of platforms
Planning of soil investigation for GBS foundation design
Characterization of in-situ effective stress profiles in clays based on piezo-cone penetration test (CPTU) results
New standards and practice of Arctic offshore soil investigation (by Russian experience)
Piezocone evaluation of undrained strength in soft to firm offshore clays
Idealized load composition for determination of cyclic undrained degradation of soils
A new piston sampler for a remotely operated drilling system
Some characteristics of carbonate sediments from North West Shelf, Western Australia
Predictive equations of shear wave velocity for Bay of Campeche sand
Strain ε50 and stiffness ratio (E50/Su) for Gulf of Mexico clays
Suitability of Masing rules for seismic analysis of offshore carbonate sediments
Simulation and experimental study of soil behaviors under principal stress rotations
Strength parameters for suction anchors in a high plasticity Ghana clay
The Maximum-Entropy Meshless method for dynamic and coupled analysis of offshore geotechnical problems
Shear wave velocity and shear modulus in offshore clays
*In situ and laboratory testing
Method dependency for determining maximum and minimum dry unit weights of sands
Shear strength of dense to very dense Dogger Bank sand
Assessment of dissipation tests in silty soils with standard and non-standard decay
Stiffness degradation and damping of carbonate and silica sands
Cyclic laboratory testing of chalk to improve the reliability of piled foundation design
Measurement and interpretation of downhole seismic probe data for estimating shear wave velocity in deep-water environments
The variation of the T-bar bearing capacity factor at shallow depths
Weak fractured rock coring via a seafloor based drilling system – a case study
Measurement uncertainty of offshore Cone Penetration Tests
An instrumented sampler and its application for suction caisson design
Comparison of shear modulus from SCPT, PS logging & laboratory tests of offshore Myanmar
Visualizing the failure surface of a laboratory vane shear in soft clay using transparent surrogate soil
A specialized triaxial testing technique for deep-sea pressure core sediments
Numerical investigation of ball penetrometer performance in dense sand overlying uniform clay
Rock-steel interface testing and considerations for gravity foundations for tidal energy generators
*Jack-up units
The effects of jack-up installation procedures on spudcan capacity in offshore carbonate sediments
A finite element study of boulder interaction with spudcans
Findings of the ISSMGE jack-up leg penetration prediction event
Finite element analyses of spudcan – subsea template interaction during jack-up rig installation
Estimation of spudcan penetration using a probabilistic Eulerian finite element analysis
Calculations of leg penetrations of heavy lift jack-up vessels in multi-layered soils
Effects of consolidation during spudcan installation in carbonate silty clay: A dual approach
Squeezing bearing capacity and effects of increasing strength with depth
Stability assessment of A-shaped mudmats of mobile production units
Linear and nonlinear foundation response in dynamic analyses of jack-up structures
Comparison of coupled and decoupled approaches to spudcan-pile interaction
Sinkage analysis of A-shaped jack-up mudmats using the Coupled Eulerian Lagrangian approach
Mariner and Gina Krog jack-up foundation challenges
A novel spudcan design for improving foundation performance
Jack-up spudcan penetration analysis: Review of semi-analytical and numerical methods
*Design, risk and reliability
A perspective on selecting design strength: Gulf of Mexico deepwater clay
Reliability-based design optimization of laterally loaded monopile foundations for offshore wind turbines
A reliability approach to cable risk assessment
Approach for the calibration of the load and resistance factors for axial pile capacity calculations
Accounting for the spatial variability of soil properties in the reliability-based design of offshore piles
Uncertainty-based characterization of piezocone and T-bar data for the Laminaria offshore site
Comparison of DNV and API design codes for design of suction anchors
به نظر من این مقاله عالی چون مقایسه دو آیین نامه می باشد جالبی این کار هر دو آنها در این موسسه کار می کنند
A safety concept for penetration analyses of suction caissons in sand
Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics II,Susan Gourvenec and David White,CRC Press,2010
این کتاب درباره سرحدهای ژئوتکنیک فراساحلی می باشد، که دارای 939 صفحه است مجموعه ای از مقالات ارسالی به دانشگاه غربی استرالیا می باشد که توسط نویسندگان جمع آوری شده است. با این عناوین
Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics II,Susan Gourvenec and David White,CRC Press,2010
The titles
This file is password
Password: CE-MS MS.c Bijan Mohammadi
All text and change the color to use to download it
دانلود / Download کلمه عبور/Password

1 Keynotes
A systematic approach to offshore engineering for multiple-project developments in geohazardous areas
Recommended best practice for geotechnical site characterisation of cohesive offshore sediments
Gulf of Guinea deepwater sediments: Geotechnical properties, design issues and installation experiences
Geotechnics for subsea pipelines
Axial and lateral pile design in carbonate soils
New frontiers for centrifuge modelling in offshore geotechnics
Risk and reliability on the frontier of offshore geotechnics
2 Geohazards and gas hydrates
Neotectonic deformation of northwestern Australia: Implications for oil and gas development
Deepwater Angola part I: Geohazard mitigation
Deepwater Angola part II: Geotechnical challenges
Shallow gas hazard linked to worldwide delta environments
Analysis of submarine flow slides in fine silty sand
Hydrate dissociation around oil exploration infrastructure
An investigation of past mass movement events in the West Nile Delta
Deformation of seabed due to exploitation of methane hydrate reservoir
3 In situ site characterisation and pore pressure measurement
A site investigation strategy to obtain fast-track shear strength design parameters in deep water soils
Enhancement of the ball penetrometer test with pore pressure measurements
Laboratory free falling penetrometer test into clay
Offshore sediment overpressures: Overview of mechanisms, measurement and modeling
Angolan deep water soil conditions: GIS technology development for sediment characterization
Strength measurement in very soft upper seabed sediments
CPT in polar snow – preliminary observations
Parametric study of a free-falling penetrometer in clay-like soils
The future of deep water site investigation: Seabed drilling technology?
Mini T-bar testing at shallow penetration
Piezometer installation in deep water Norwegian Sea
Luva deep water site investigation programme and findings
Investigations into novel shallow penetrometers for fine-grained soils
Seabed drilling vs surface drilling – a comparison
4 Soil characterisation and modelling
Rheological behaviour of soft clays
A three-dimensional finite element study of the direct simple shear test
Repeated loading and unloading of the seabed
A new interpretation of the simple shear test
Physical modelling of the crushing behaviour of granular materials
New evidence for the origin and behaviour of deep ocean ‘crusts’
Soil unit weight estimated from CPTu in offshore soils
Strain rate dependent simple shear behaviour of deep water sediments in offshore Angola
Simplified calibration procedure for a high-cycle accumulation model based on cyclic triaxial tests on 22 sands
Understanding cyclic loading behavior of soil for offshore applications
5 Shallow foundations
Observations of shallow skirted foundations under transient and sustained uplift
Numerical study of grillage foundations on sand under combined VHM loading
The vertical bearing capacity of grillage foundations in sand
Behaviour of skirted footings on sand overlying clay
Numerical study of piping limits for suction installation of offshore skirted foundations and anchors in layered sand
Shallow foundation performance in a calcareous sand
A numerical study of the vertical bearing capacity of skirted foundations
The effect of torsion on the sliding resistance of rectangular foundations
Foundation design challenges of the MCR-A skirted gravity platform
Constructing breakwater with prefabricated caissons on soft clay
6 Piled foundations
Simplified analysis of laterally loaded pile groups
Behavior of piles under combined lateral and axial loading
Investigations on the behavior of large diameter piles under cyclic lateral loading
BP Clair phase 1 – Pile driveability and capacity in extremely hard till
Photoelastic investigation into plugging of open ended piles
Soil-pile interaction during extrusion of an initially deformed pile
BP Clair phase 1 – Geotechnical assurance of driven piled foundations in extremely hard till
Pile driving experiences in Persian Gulf calcareous sands
FLAC3D analysis on soil moving through piles
Cyclic loading of barrettes in soft calcareous rock using Osterberg cells
Shaft capacity of drilled and grouted piles in calcareous sandstone
Numerical analysis of mudmat contribution to capacity of piled offshore platforms
Simplified numerical model for analysis of offshore piles under cyclic lateral loading
Centrifuge modelling of rapid load tests with piles in silt and sand
Field measurements on monopile Dolphins
Behaviour of driven tubular steel piles in calcarenite for a marine jetty in Fujairah, United Arab Emirates
CPT-Based design method for axial capacity of offshore piles in clays
7 Foundations for renewable energy
Evaluation of pile capacity approaches with respect to piles for wind energy foundations in the North Sea
Installation of suction caissons for offshore renewable energy structures
Lateral behaviour of large diameter monopiles at Sheringham Shoal Wind Farm
Centrifuge modelling of offshore monopile foundation
Gravity based foundations for the Rødsand 2 offshore wind farm, Denmark
Geotechnics for developing offshore renewable energy in the US
Engineering issues for fixed offshore wind turbines on Lake Michigan Mid Lake Plateau, USA
Centrifuge model tests on piled footings in clay for offshore wind turbines
Design of monopile foundations in sand for offshore windfarms
Experimental evaluation of backfill in scour holes around offshore monopoles
An investigation of the use of a bearing plate to enhance the lateral capacity of monopile foundations
Optimizing site investigations and pile design for wind farms using geostatistical methods: A case study
Towards the FE prediction of permanent deformations of offshore wind power plant foundations using a high-cycle accumulation model
Cyclic accumulation effects at foundations for offshore wind turbines
Study on soil-structure interaction of suction caisson by large-scale model tests
8 Jack-up units
Simplified VH equations for foundation punch-through sand into clay
Characterisation of undrained shear strength using statistical methods
Centrifuge modelling of spudcan deep penetration in multi-layered soils
A probabilistic approach to the prediction of spudcan penetration of jack-up units
An assessment of jackup spudcan extraction
3D FE analysis of the installation process of spudcan foundations
Undrained bearing capacity of deeply embedded foundations under general loading
9 Anchoring systems
Trajectory prediction for drag embedment anchors under out of plane loading
Setup following keying of plate anchors assessed through centrifuge tests in kaolin clay
Seismically-induced displacements of a suction caisson in soft clay
SEPLA keying prediction method based on full-scale offshore tests
Set-up of suction piles in deep water Gulf of Guinea clays
Centrifuge testing of suction piles in deep water Nigeria clay – Effect of stiffeners and set-up time
Numerical FEM and laboratory study of the bearing capacity factor Nc for plate anchors
Caisson capacity in clay: VHM resistance envelope – Part 2: VHM envelope equation and design procedures
Installation and in-place assessment of drag anchors in carbonate soil
Caisson capacity in clay: VHM resistance envelope – Part 1: 3D FEM numerical study
Numerical investigation of the behaviour of suction caissons in structured clays
Cyclic moment loading of suction caissons in sand
10 Pipelines and risers
Multidirectional analysis of pipeline-soil interaction in clay
Geotechnical challenges for deep water pipeline design – SAFEBUCK JIP
Large deformation finite element analysis of vertical penetration of pipelines in seabed
Implementation of geotechnical techniques in the analysis of pipeline response
Lateral soil resistance to an untrenched pipeline under the action of ocean currents
Vertical cyclic testing of model steel catenary riser at large scale
Kupe gas project pipeline – optimisation of discrete rock berm design shore approach
Model test studies on soil restraint to pipelines buried in sand
Pipe-soil interaction on clay with a variable shear strength profile
Sweeping behaviour of shallowly-embedded pipeline during cyclic lateral movement
Advanced nonlinear hysteretic seabed model for dynamic fatigue analysis of steel catenary risers
Mobilization distance in uplift resistance modeling of pipelines
Theoretical, numerical and field studies of offshore pipeline sleeper crossings
Observations of pipe-soil response from the first deep water deployment of the SMARTPIPE®
11 Trenching, ploughing, excavation and burial
Influence of object geometry on penetration into the seabed
Investigation into the effect of forecutters on plough performance
State-of-the-art jet trenching analysis in stiff clays
Numerical modelling of soil around offshore pipeline plough shares
Anchor–chain–rock fill–soil interaction: Evolution of design methods
Development of a jet trenching model in sand
12 Design and risk
Structural factors affecting the system capacity of jacket pile foundations
The new API Recommended Practice for Geotechnical Engineering: RP 2GEO
Comparison of ISO 19901-2 and API RP 2A seismic design criteria for a site in the Caspian Sea, Turkmenistan

Offshore Engineering-An Introduction 2nd Endition, by Angus Mather, witherby & Company Limited, 2000
برای اولین بار این کتاب در سال 1995 به چاپ رسید بعد 5 سال دوباره ویرایش شد می تواند گفت این کتاب هم در زمان خودش و زمان حال بهترین کتاب فراساحلی می باشد. فایلی اسکن شده است که در وبلاگ دنیای سازه های دریایی موجود می باشد بهینه شده و قابلیت جستجو در فایل را داراه می باشد.
This is book Offshore Engineering-An Introduction 2nd Endition, by Angus Mather, witherby & Company Limited, 2000
All text and change the color to use to download it
Download / دانلود کلمه عبور/ Password

نویسنده، این کتاب آنگوس ماتر کار خود را در وزارت صنایع دفاع بریتانیا در کارخانه کشتی سازی در سال 1970 به عنوان یک شاگرد تکنیسین آغاز کرد که این شغل به مدت 10 سال ادامه داشت بعد از آن به عنوان افسر مهندس در نیروی دریایی بریتانیا مشغول به کار بود بعد از 15 سال بعد وارد صنعت نفت و گاز و صنعت پیمانکاری شد به عنوان مدیرمهندس نفت به کار گرفته شد، و همچنین به عنوان یک مهندس نقشه بردار برای (LR) (موسسه بریتانیای است برای صدور گواهینامه اطمینان از کیفیت ساخت و ساز ، ایمنی از جان مال، محیط زیست ،طبقه بندی استانداردهای دریایی می باشد.) با توجه به شرایط نویستده ایشان درگیر با کارهای نفتی و پروژه های مربوط به گاز داشته که این کارها در قسمت فراساحل انگلستان، خاورمیانه و خیلج مکزیک بوده
The author, Angus Mather commenced his Career with the Ministry of Defence at Her Majesty 's Dockyard, Devonport , in 1970 as a Technician Apprentice. This was followed by 10 years’ service as an Engineer Officer in the British Merchant Navy prior to entering the oil and gas industry. The next 15years were spent employed both in the contracting industry as Engineering Manager of Kvaerner Oil and Gas Services , and as an engineer Surveyor for Lloyds Register of Shipping, involved with oil and gas related projects , both on and offshore, in the UK, the Middle East and the Gulf of Mexico
Chapter One- offshore structures and support vessels
Chapter Two- The North sea History and legislation
Chapter Three- Safety systems
Chapter Four- Piping systems and process pressure vessels
Chapter Five –production
Chapter Six- Underwater Engineering
Chapter Seven- Drilling
Chapter Eight-The well component parts
Support vessel, Fuel Gas, Fixed Steel Structures, Vent, The North sea, wet Gas, Safety management system, wellheads, Gas Injection, cement job, Top Drive, Christmas Tree
Chapter Nine-Well Maintenance